Purim dosages:
Purim packs:

Purchase 60 caps purim overnight delivery
Chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia this is outlined by a persistent monocytosis of more than 1. Bruising is frequent and gum hypertrophy Chapter sixteen: Myelodysplasia / 185 Myelodysplasia features a group of clonal disorders of haemopoietic stem cells that lead to bone marrow failure and low blood cell counts. A hallmark of the illness is the increased proliferation and apoptosis of haemopoietic cells resulting in the paradox of a hypercellular bone marrow but pancytopenia. In most instances, the disease is main however it may be secondary to chemotherapy or radiotherapy given for therapy of another malignancy. The primary scientific features of anaemia, an infection and bleeding, are brought on by reduction in the blood rely. Diagnosis is made by examination of the blood and bone marrow together with cytogenetic and molecular genetic research of the tumour cells. Scoring methods can divide sufferers into these with lowgrade or highgrade disease. Haemopoietic progress elements, lenalidomide or blood product support are useful when required. Highgrade myelodysplasia may be treated by intensive chemotherapy, demethylating drugs or stem cell transplantation. Myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms are a gaggle of problems categorized between myelodysplasia and myeloproliferative issues and show the presence of dysplastic options but additionally increased variety of circulating white cells. Studies in identical twins have shown that both may be born with the identical chromosomal abnormality. This has presumably arisen spontaneously in a progenitor cell that has passed from one twin to the other as a outcome of the shared placental circulation. In different instances, the disease seems to come up as a postnatal mutation in an early lymphoid progenitor cell. Certain germline polymorphisms in a bunch of genes mainly involved in Bcell development. Bone marrow failure Anaemia (pallor, lethargy and dyspnoea); Neutropenia (fever, malaise, options of mouth, throat, skin, respiratory, perianal or different infections); Thrombocytopenia (spontaneous bruises, purpura, bleeding gums and menorrhagia). The subtype is an important guide to the optimum remedy protocol and to prognosis. Investigations Haematological investigations reveal a normochromic normocytic anaemia with thrombocytopenia in most cases. The whole white cell rely may be decreased, regular or elevated to 200 � 109/L or more. Biochemical exams may reveal a raised serum uric acid, serum lactate dehydrogenase or, less generally, hypercalcaemia. Liver and renal function tests are performed as a baseline before remedy begins. Cytogenetics and molecular genetics Cytogenetic evaluation shows differing frequencies of abnormalities in infants, children and adults which partly explains the completely different prognoses of these teams. The incidence of various cytogenic abnormalities in infants, youngsters and adults. Chapter 17: Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia / 191 stratified in accordance with the number of chromosomes in the tumour cell (ploidy) or by particular molecular abnormalities. Hyperdiploid cells have greater than 50 chromosomes and usually have a great prognosis whereas hypodiploid cases (less than forty four chromosomes) carry a poor prognosis. These molecular genetic adjustments carry prognostic significance whether or not a corresponding chromosomal change is present. General supportive remedy General supportive remedy for bone marrow failure is described in Chapter 12 and contains the insertion of a central venous cannula, blood product assist and prevention of tumour lysis syndrome. The risk of tumour lysis syndrome is highest in youngsters with a excessive white cell depend, Tcell disease or concurrent renal impairment at presentation. There are several phases in a remedy course, which often has four elements. The protocols are danger adjusted to cut back the remedy given to patients with good prognosis.
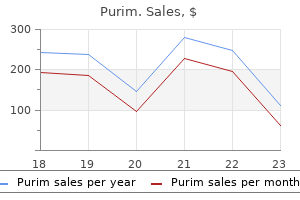
Discount purim generic
Collectins play a job in the innate immune system by acting as microbial sample recognition receptors, they usually could activate the complement system by binding to C1q. Complement A system of serum and cell floor proteins that interact with one another and with other molecules of the immune system to generate essential effectors of innate and adaptive immune responses. The classical, various, and lectin pathways of the complement system are activated by antigen-antibody complexes, microbial surfaces, and plasma lectins binding to microbes, respectively, and include a cascade of proteolytic enzymes that generate inflammatory mediators and opsonins. These hypervariable segments assume loop constructions that together type a floor complementary to the three-dimensional structure of the sure antigen. Congenital immunodeficiency A genetic defect by which an inherited deficiency in some aspect of the innate or adaptive immune system leads to an increased susceptibility to infections. Congenital immunodeficiency is frequently manifested early in infancy and childhood however is sometimes clinically detected later in life. Contact sensitivity A state of immune responsiveness to sure chemical brokers leading to T cell�mediated delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions upon pores and skin contact. Other costimulators bind to receptors that are expressed on activated T cells, resulting in enhanced effector responses. CpG nucleotides are recognized by Toll-like receptor 9, they usually have adjuvant properties within the mammalian immune system. The take a look at entails mixing the recipient serum with leukocytes or pink blood cells from potential donors and analyzing for agglutination or complement-dependent lysis of the cells. C-type lectin A member of a big family of calciumdependent carbohydrate-binding proteins, a lot of which play important roles in innate and adaptive immunity. For instance, soluble C-type lectins bind to microbial carbohydrate constructions and mediate phagocytosis or complement activation. Cutaneous immune system the parts of the innate and adaptive immune system found within the pores and skin that function collectively in a specialized way to detect and respond to pathogens on or in the pores and skin and to maintain homeostasis with commensal microbes. Components of the cutaneous immune system embrace keratinocytes, Langerhans cells, dermal dendritic cells, intraepithelial lymphocytes, and dermal lymphocytes. Cyclosporine A calcineurin inhibitor widely used as an immunosuppressive drug to forestall allograft rejection by blocking T cell activation. Cytokines Proteins which are produced and secreted by many various cell varieties, and mediate inflammatory and immune reactions. Dectins Pattern recognition receptors expressed on dendritic cells that acknowledge fungal cell wall carbohydrates and induce signaling occasions that promote irritation and enhance adaptive immune responses. Defensins Cysteine-rich peptides produced by epithelial barrier cells within the skin, gut, lung, and other tissues and in neutrophil granules that act as broad-spectrum antibiotics to kill a wide variety of micro organism and fungi. Dendritic cells Bone marrow�derived cells found in epithelial and lymphoid tissues that are morphologically characterised by skinny membranous projections. Immature (resting) classical dendritic cells are essential for induction of tolerance to self antigens. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells produce abundant sort 1 interferons in response to publicity to viruses. Desensitization A method of treating immediate hypersensitivity illness (allergies) that includes repetitive administration of low doses of an antigen to which individuals are allergic. Determinant the specific portion of a macromolecular antigen to which an antibody or T cell receptor binds. DiGeorge syndrome A selective T cell deficiency attributable to a congenital malformation that results in defective growth of the thymus, parathyroid glands, and other constructions that come up from the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches. Direct presentation is partly answerable for strong T cell responses to allografts. Diversity the existence of numerous lymphocytes with completely different antigenic specificities in any particular person. Random use of D segments contributes to the variety of the antigen receptor repertoire. Ectoparasites Parasites that stay on the floor of an animal, corresponding to ticks and mites. Both the innate and adaptive immune methods might play a job in protection against ectoparasites, often by destroying the larval phases of those organisms. Effector cells the cells that carry out effector functions during an immune response, corresponding to secreting cytokines.
Diseases
- Neonatal diabetes mellitus, transient (TNDM)
- Der Kaloustian Mcintosh Silver syndrome
- Sacrococcygeal dysgenesis association
- Choledochal cyst, hand malformation
- Nonsyndromic hereditary hearing impairment
- Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita
- Acropectorenal field defect
- Marfan-like syndrome
- PHACE association
Order 60caps purim overnight delivery
The movement of leukocytes within numerous tissues is often directed by gradients of low�molecular-weight cytokines called chemokines. When T cells are engineered to express chimeric antigen receptors these cells can acknowledge and kill cells that the extracellular area recognizes. Chromosomal translocation A chromosomal abnormality during which a phase of one chromosome is transferred to one other. The disease is characterized by recurrent intracellular bacterial and fungal infections, usually accompanied by chronic cell-mediated immune responses and the formation of granulomas. Chronic rejection A form of allograft rejection characterized by fibrosis with loss of regular organ buildings occurring during a prolonged interval. In many instances, the major pathologic event in continual rejection is graft arterial occlusion caused by proliferation of intimal easy muscle cells, which is called graft arteriosclerosis. The classical pathway is initiated by binding of antigen-antibody complexes to the C1 molecule, resulting in proteolytic cleavage of C4 and C2 proteins to generate the classical pathway C3 convertase. The classical pathway, as well as the choice and lectin pathways, terminates with formation of the membrane attack complicated. Clonal anergy A state of antigen unresponsiveness of a clone of T lymphocytes experimentally induced by recognition of antigen within the absence of extra indicators (costimulatory signals) required for functional activation. Clonal anergy is considered a mannequin for one mechanism of tolerance to self antigens and may be applicable to B lymphocytes as nicely. Clonal deletion A mechanism of lymphocyte tolerance by which an immature T cell within the thymus or an immature B cell within the bone marrow undergoes apoptotic demise as a consequence of recognizing a self antigen. Clonal expansion the approximately 1000- to a hundred,000fold enhance in variety of lymphocytes specific for an antigen that results from antigen stimulation and proliferation of naive T and B cells. Clonal enlargement occurs in lymphoid tissues and is required to generate enough antigen-specific effector T lymphocytes and plasma cells from rare naive precursors to eradicate infections. Clonal ignorance A form of lymphocyte unresponsiveness by which self antigens are ignored by the immune system even though lymphocytes specific for these antigens stay viable and functional. Clonal choice hypothesis A fundamental tenet of the immune system (no longer a hypothesis) stating Glossary 495 that every individual possesses numerous clonally derived lymphocytes, every clone having arisen from a single precursor, expresses one antigen receptor, and is able to recognizing and responding to a definite antigenic determinant. Clone A group of cells, all derived from a single common precursor, which preserve lots of the genotypic and phenotypic features shared by the cell of origin. Coinhibitor A cell surface protein expressed by antigenpresenting cells or tissue cells that binds to coinhibitory receptors on effector T cells, inducing alerts that block T cell activation by antigen and costimulators. Effector phase the part of an immune response by which a foreign antigen is destroyed or inactivated. For example, in a humoral immune response, the effector section could also be characterised by antibodydependent complement activation and phagocytosis of antibody- and complement-opsonized bacteria. Endosome An intracellular membrane-bound vesicle into which extracellular proteins are internalized during antigen processing. Endotoxin incorporates both lipid components and carbohydrate (polysaccharide) moieties. In cells of the immune system, enhancers are responsible for integrating cell surface signals that lead to induced transcription of genes encoding most of the effector proteins of an immune response, corresponding to cytokines. Eosinophils are necessary in protection against extracellular parasites, including helminths. Epitope the particular portion of a macromolecular antigen to which an antibody or T cell receptor binds. Epitope spreading In autoimmunity, the development of immune responses to multiple epitopes as an autoimmune disease initially targeting one epitope progresses, doubtless brought on by additional breakdown in tolerance and launch of extra tissue antigens as a outcome of the inflammatory course of stimulated by the preliminary response. Fab (fragment, antigen-binding) A part of an antibody, first produced by proteolysis of IgG, that includes one complete light chain paired with one heavy chain fragment containing the variable area and only the primary fixed area. Therefore, Fab preparations are utilized in research and therapeutic applications when antigen binding is desired with out activation of effector functions. They are used in analysis and therapeutic applications when antigen binding is desired without antibody effector functions. The dying pathway is initiated when Fas binds to Fas ligand expressed on activated T cells.
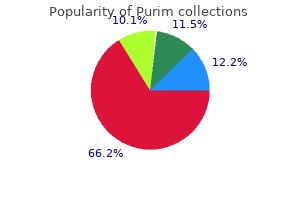
Discount purim 60 caps with amex
There is also evidence that oral or parenteral iron may scale back fatigue in irondeficient (low serum ferritin) nonanaemic ladies. Urine, sweat, faeces Adult male Postmenopausal feminine Menstruating female* Pregnant female* Children (average) Female (age 12�15)* 0. Reticuloendothelial (macrophage) stores are misplaced completely earlier than anaemia develops. Menorrhagia (a lack of eighty mL or extra of blood at each cycle) is tough to assess clinically, although the lack of clots, the use of giant numbers of pads or tampons or prolonged durations all counsel excessive loss. It takes about eight years for a traditional grownup male to develop iron deficiency anaemia solely because of a poor diet or malabsorption leading to no iron intake at all. In developed international locations insufficient intake or malabsorption are only not often the only reason for iron deficiency anaemia. Gluteninduced enteropathy, partial or complete gastrectomy and atrophic gastritis (often autoimmune and with Helicobacter pylori infection) may, nonetheless, predispose to iron deficiency. In creating coun tries, iron deficiency could occur on account of a lifelong poor diet, consisting primarily of cereals and vegetables. Hookworm Gluteninduced enteropathy, gastrectomy, autoimmune gastritis Poor food regimen A major factor in many developing countries but rarely the sole trigger in developed nations could irritate iron deficiency, as might repeated pregnancies or growth and menorrhagia in young females. Laboratory findings these are summarized and contrasted with those in other hypochromic anaemias in Table 3. Red cell indices and blood film Even earlier than anaemia happens, the red cell indices fall and so they fall progressively because the anaemia turns into extra severe. The blood film exhibits hypochromic, microcytic cells with occasional goal cells and pencilshaped poikilocytes. The platelet depend is often moderately raised in iron deficiency, notably when haemorrhage is constant. In iron deficiency anaemia the serum ferritin may be very low whereas a raised serum ferritin indicates iron overload or excess release of ferritin from damaged tissues or an acute part response. In men and postmenopausal women, gasoline trointestinal blood loss is the main explanation for iron deficiency and the precise website is sought from the scientific historical past, physical and rectal examination, by occult blood checks, and by applicable use of higher and decrease gastrointestinal endoscopy and/or radi ology. Tests for parietal cell antibodies, Helicobacter infec tion and serum gastrin level could help to diagnose autoimmune gastritis. In troublesome circumstances a digicam in a capsule may be swal lowed which relays pictures of the gastrointestinal tract elec tronically. Tests for transglutaminase antibodies and duodenal biopsy to search for gluteninduced enteropathy can be valuable. Hookworm ova are sought in stools of subjects from areas the place this infestation occurs. Two populations of purple cells are current: one microcytic and hypochromic, the opposite normocytic and properly haemoglobinized. Serum ferritin A small fraction of physique ferritin circulates within the serum, the concentration being associated to tissue, particularly reticulo endothelial, iron stores. In some laboratories, the transferrin content of serum is measured instantly by immunodiffusion, rather than by its capacity to bind iron, and is expressed in g/L. Normal serum accommodates 2�4 g/L transferrin (1 g/L transferrin = 20 mol/L binding capacity). Oral iron the most effective preparation is ferrous sulphate which is cheap, con tains 67 mg iron in every 200mg pill and is greatest given on an empty stomach in doses spaced by a minimum of 6 hours. Continuing haemorrhage Failure to take tablets Wrong prognosis � especially thalassaemia trait, sideroblastic anaemia Mixed deficiency � related folate or vitamin B12 deficiency Another trigger for anaemia. Intra venous iron has additionally been found to increase functional capac ity and high quality of life in some patients with congestive coronary heart failure, even within the absence of anaemia (see p. There could also be a haematologi cal response to intravenous however often to not oral iron. Oral iron remedy ought to be given for lengthy sufficient both to appropriate the anaemia and to replenish physique iron shops, which usually means for a minimum of 6 months. Iron for tification of the diet in infants in Africa reduces the incidence of anaemia but increases suceptibility to malaria. Parenteral iron Many totally different preparations can be found with various licens ing in different countries.
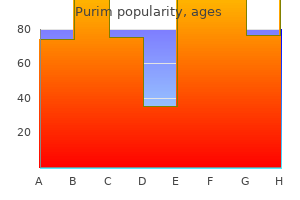
60 caps purim with mastercard
Percutaneous gadget closure in the cardiac catheterization laboratory may be performed in select patients with an unacceptable surgical danger. Patients must be instructed to seek extra frequent or pressing follow-up evaluation if they experience any noticeable adjustments of their medical status. Specific plans for long-term follow-up care ought to be individualized primarily based on clinical status, anatomy, prior interventions, and alter in symptoms. Estimated 1- and 5-year mortality are 30% and 50%, respectively (Circulation 2010;123(4): 410-528). Other risk components with high population attributable danger embody tobacco use, hypertension, diabetes, and weight problems (Circulation 2014;131:e29-e322). Marked limitation in exercise due to symptoms, even throughout less than odd exercise (walking short distances [20-100 m]). The sympathetic nervous system can be activated, with increased ranges of circulating catecholamines, resulting in elevated myocardial contractility. Over time, these neurohormonal pathways end in direct mobile toxicity, fibrosis, arrhythmias, and pump failure. Cardiac dysfunction and pathologic transforming alter the ventricular pressure-volume relationship, resulting in an increase in chamber pressures, leading to pulmonary and systemic venous congestion. Extreme decompensation could present as cardiogenic shock (resulting from each low arterial and excessive venous pressures), characterised by hypoperfusion of important organs, resulting in renal failure (decreased urine output), mental status modifications (confusion and lethargy), or "shock liver" (elevated liver perform tests). Venous pulsations are differentiated from carotid pulsation by their biphasic nature, respiratory variability, and compressibility. Abdominojugular reflux suggests an impaired ability of the right ventricle to handle augmented preload and may be because of constriction or pulmonary hypertension in addition to myocardial illness. Low cardiac output is recommended by a proportional pulse strain (pulse pressure/diastolic blood pressure) 25%, diminished carotid upstroke, and cool extremities. Imaging Chest radiography should be carried out to consider the presence of pulmonary edema or cardiomegaly and rule out different etiologies of dyspnea. Right heart catheterization with placement of a pulmonary artery catheter may assist information remedy in sufferers with hypotension and evidence of shock. Endomyocardial biopsy ought to be thought-about when seeking a particular prognosis that would influence therapy, particularly in sufferers with rapidly progressive and unexplained cardiomyopathy, these in whom energetic myocarditis, particularly big cell myocarditis, is taken into account, and people with potential infiltrative processes corresponding to cardiac amyloidosis and sarcoidosis (Circulation 2007;116:2216-33). Individual -blockers have distinctive properties, and the useful impact of -blockers may not be a class impact. Renal function and potassium levels should be monitored with dose adjustment and periodically with persistent use. Additional adverse effects may embrace cough, rash, angioedema, dysgeusia, enhance in serum creatinine, proteinuria, hyperkalemia, and leukopenia. Eplerenone is a selective aldosterone receptor antagonist without the estrogenic side effects of spironolactone. The potential for growth of life-threatening hyperkalemia exists with the usage of these agents. Gynecomastia may develop in 10-20% of men treated with spironolactone; eplerenone should be used on this case. Vasodilator therapy alters preload and afterload situations to improve cardiac output. Hydralazine acts directly on arterial easy muscle to produce vasodilation and to cut back afterload. Nitrates are predominantly venodilators and help relieve symptoms of venous and pulmonary congestion. They additionally reduce myocardial ischemia by decreasing ventricular filling pressures and by directly dilating coronary arteries. Reflex tachycardia and increased myocardial oxygen consumption might happen within the setting of hydralazine use, requiring cautious use in patients with ischemic heart illness. Digoxin has a slender therapeutic index, and serum ranges must be followed carefully, notably in patients with unstable renal function. Agents which will improve levels include erythromycin, tetracycline, quinidine, verapamil, flecainide, and P. Electrolyte abnormalities (particularly hypokalemia), hypoxemia, hypothyroidism, renal insufficiency, and quantity depletion can also exacerbate toxicity. Frequent complications of remedy embrace hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypomagnesemia, volume contraction alkalosis, intravascular volume depletion, and hypotension.
Syndromes
- Heroin
- Impotence
- Malnutrition (when severe)
- Does the person use alcohol? How much?
- Fuse the joint together to make the toe straight and no longer able to bend.
- Mental status changes
- Increased sweating
- Medicines used for depression or psychosis
- Eye pain
- Bilirubin level is high
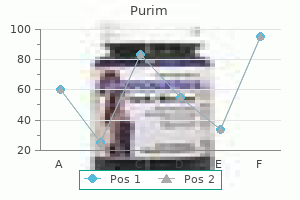
Order purim online from canada
Les s er trochanter Patellar ligament the patellar ligament is functionally the continuation of the quadriceps femoris tendon beneath the patella and is hooked up above to the apex and margins of the patella and beneath to the tibial tuberosity. The extra supercial bers of the quadriceps femoris tendon and the patellar ligament are continuous over the anterior floor of the patella, and lateral and medial bers are steady with the ligament beside the margins of the patella. All besides the pectineus, which is innervated by the femoral nerve, and part of the adductor magnus, which is innervated by the sciatic nerve, are innervated by the obturator nerve. Collectively, all these muscles besides the obturator externus mainly adduct the thigh on the hip joint; the adductor longus and magnus may medially rotate the thigh. Obturator externus is a lateral rotator of the thigh on the hip joint and the gracilis also exes the leg at the knee joint. The adductor magnus is the most important and deepest of the muscular tissues within the medial compartment of thigh. It is a triangular or fan-shaped muscle anchored by its apex to the pelvis and connected by its expanded base to the femur. The medial a part of the adductor magnus, often known as the "hamstring part," originates from the ischial tuberosity of the pelvic bone and descends almost vertically along the thigh to insert by way of a rounded tendon into the adductor tubercle on the medial condyle of the distal head of the femur. The lateral or adductor part of the muscle inserts by way of an aponeurosis up onto the medial supracondylar line. A giant circular gap inferiorly between the hamstring and adductor parts of the muscle is the adductor hiatus. The adductor part of the muscle is innervated by the obturator nerve and the hamstring half is innervated by the tibial division of the sciatic nerve. As a gaggle, the hamstrings ex the leg on the knee joint and prolong the thigh at the hip joint. Typical causes could include limb trauma, intracompartment hemorrhage, and limb compression. As strain throughout the compartment elevates, capillary blood ow and tissue perfusion is compromised, which can ultimately result in neuromuscular injury if not handled. Clinical app Hamstring accidents Hamstring accidents embody tendon avulsion at the ischial tuberosity, and intermuscular, musculotendinous, and myofascial disruptions inside the muscle bellies. Among the common causes of these accidents are water skiing (hamstring tendon avulsion), monitor and eld occasions, soccer and soccer injuries and fast dash injuries (muscle belly injuries). Arteries Three arteries enter the thigh: the femoral artery, the obturator artery, and the inferior gluteal artery. The three arteries contribute to an anastomotic community of vessels around the hip joint. B 296 Regional anatomy � Thigh passes under the inguinal ligament to enter the femoral triangle on the anterior side of the higher thigh. The femoral artery passes vertically via the femoral triangle and then continues down the thigh within the adductor canal. It leaves the canal by passing by way of the adductor hiatus within the adductor magnus muscle and turns into the popliteal artery behind the knee. A cluster of 4 small branches-super cial epigastric artery, tremendous cial circum ex iliac artery, supercial exterior pudendal artery, and deep external pudendal artery-originate from the femoral artery in the femoral triangle and provide cutaneous regions of the higher thigh, lower abdomen, and perineum. The major trunk of the medial circum ex femoral artery passes over the superior margin of the adductor magnus and divides into two major branches deep to the quadratus femoris muscle: One department ascends to the trochanteric fossa and connects with branches of the gluteal and lateral circum ex femoral arteries. The other department passes laterally to take part with branches from the lateral femoral circum ex artery, the inferior gluteal artery, and the rst perforating artery in forming an anastomotic community of vessels across the hip. The deep artery of thigh immediately passes: posteriorly between the pectineus and adductor longus muscle tissue and then between the adductor longus and adductor brevis muscle tissue; and then travels inferiorly between the adductor longus and adductor magnus, ultimately penetrating via the adductor magnus to connect with branches of the popliteal artery behind the knee. The deep artery of thigh has lateral and medial circumex femoral branches and three perforating branches. Perforating arteries the three perforating arteries branch from the deep artery of thigh. All three penetrate through the adductor magnus near its attachment to the linea aspera to enter and supply the posterior compartment of thigh. Here, the vessels have ascending and descending branches, which interconnect to kind a longitudinal channel, which participates above in forming an anastomotic network of vessels across the hip and inferiorly anastomoses with branches of the popliteal artery behind the knee. Obturator artery the obturator artery originates as a department of the internal iliac artery within the pelvic cavity and enters the medial compartment of thigh through the obturator canal. As it passes through the canal, it bifurcates into Lateral circum ex femoral artery the lateral circum ex femoral artery usually originates proximally from the lateral aspect of the deep artery of thigh, but may come up directly from the femoral artery.
Generic 60 caps purim with mastercard
It offers rise to a series of progressively smaller normoblasts by a variety of cell divisions. A completely pinkstaining mature erythrocyte results which is a nonnucleated biconcave disc. They appear in the blood if erythropoiesis is going on outdoors the marrow (extramedullary erythropoiesis) and in addition with some marrow ailments. Normally, 90% of the hormone is produced in the peritubular interstitial cells of the kidney and 10% in the liver and elsewhere. Erythropoietin manufacturing subsequently will increase in anaemia, and likewise when haemoglobin for some metabolic or structural cause is unable to surrender O2 usually, when atmospheric O2 is low or when defective cardiac or pulmonary operate or damage to the renal circulation impacts O2 delivery to the kidney. Erythropoietin stimulates erythropoiesis by rising the variety of progenitor cells dedicated to erythropoiesis. In infants, the marrow cavity could increase into cortical bone leading to bone deformities with frontal bossing and protrusion of the maxilla (see p. Conversely, increased O2 provide to the tissues (because of an increased purple cell mass or as a end result of haemoglobin is prepared to launch its O2 extra readily than normal) reduces the erythropoietin drive. They are high in anaemia except this is as a outcome of of renal failure and if a tumour secreting erythropoietin is current, but low in severe renal illness or polycythaemia vera. It is given subcutaneously either thrice weekly or as quickly as each 1�2 weeks or each four weeks, relying on the indication and on the preparation used (erythropoietin alpha or beta, darbepoetin alpha (a heavily glycosylated longeracting form), or Micera the longest appearing preparation). A low serum erythropoietin stage prior to therapy is efficacious in predicting an efficient response. Sideeffects include an increase in blood pressure, thrombosis and native injection site reactions. It has been associated with progression of some tumours which express Epo receptors. These embrace metals such as iron and cobalt, nutritional vitamins (especially vitamin B12, folate, vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin B6, thiamine and riboflavin) and hormones corresponding to androgens and thyroxine. In order to obtain this gaseous trade they contain the specialised protein haemoglobin. Each molecule of regular adult haemoglobin A (Hb A) (the dominant haemoglobin in blood after the age of 3�6 months) consists of 4 polypeptide chains, 22, each with its own haem group. Normal adult blood also contains small quantities of two other haemoglobins: Hb F and Hb A2. These also include chains, but with and chains, respectively, instead of (Table 2. The synthesis of the various globin chains in the fetus and grownup is discussed in additional detail in Chapter 7. Anaemia of persistent renal illness Myelodysplastic syndrome Anaemia associated with malignancy and chemotherapy Anaemia of continual diseases. The mitochondria are the main websites of protoporphyrin synthesis, iron (Fe) is equipped from circulating transferrin; globin chains are synthesized on ribosomes. Ultimately, protoporphyrin combines with iron in the ferrous (Fe2+) state to form haem. As the haemoglobin molecule loads and unloads O2 the individual globin chains move on each other. This motion is answerable for the sigmoid form of the haemoglobin O2 dissociation curve. Normally, in vivo, O2 change operates between 95% saturation (arterial blood) with a mean arterial O2 pressure of ninety five mmHg and 70% saturation (venous blood) with a imply venous O2 tension of 40 mmHg. Methaemoglobinaemia it is a medical state in which circulating haemoglobin is current with iron in the oxidized (Fe3+) instead of the usual Fe2+ state. It might arise because of a hereditary deficiency of methaemoglobin reductase deficiency or inheritance of a structurally irregular haemoglobin (Hb M). Hb Ms comprise an amino acid substitution affecting the haem pocket of the globin chain. Toxic methaemoglobinaemia (and/or sulphaemoglobinaemia) occurs when a drug or other poisonous substance oxidizes haemoglobin. The purple cell In order to carry haemoglobin into shut contact with the tissues and for profitable gaseous trade, the pink cell, eight m in diameter, must be able: to cross repeatedly through the microcirculation whose minimum diameter is three. A single journey round the physique takes 20 seconds and its total journey throughout its 120day lifespan has been estimated to be 480 km (300 miles).

Trusted purim 60caps
The pudendal nerve is the major somatic nerve of the perineum and has no branches in the gluteal area. Inferior gluteal nerve the inferior gluteal nerve enters the gluteal region through the higher sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis muscle and along the posterior floor of the sciatic nerve. It is a small nerve that leaves the sacral plexus in the pelvic cavity by piercing the sacrotuberous ligament. It then loops around the decrease border of the gluteus maximus to supply pores and skin over the medial aspect of the gluteus maximus. Firs t perforating artery from deep artery of thigh the superior gluteal nerve and vessels normally enter the gluteal region above the piriformis and move superiorly and ahead. The anterior corner of the higher lateral quadrant is often used for injections to avoid injuring any part of the sciatic nerve or different nerves and vessels within the gluteal region. A needle placed on this region enters the gluteus medius anterosuperior to the margin of the gluteus maximus. Superior gluteal artery Inferior gluteal artery Arteries Inferior gluteal artery the inferior gluteal artery originates from the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery in the pelvic cavity. It leaves the pelvic cavity by way of the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis muscle. The inferior gluteal artery provides adjacent muscles and descends via the gluteal region and into the posterior thigh the place it provides adjacent buildings and anastomoses with perforating branches of the femoral artery. Lateral femoral circumflex artery Medial femoral circumflex artery Deep artery of thigh Firs t perforating artery Femoral artery Second perforating artery Superior gluteal artery the superior gluteal artery originates from the posterior trunk of the internal iliac artery within the pelvic cavity. It leaves the pelvic cavity through the larger sciatic foramen above the piriformis muscle. In the gluteal area, it divides into an excellent cial department and a deep department: the super cial branch passes onto the deep surface of the gluteus maximus muscle. Regional anatomy � Thigh In addition to adjacent muscles, the superior gluteal artery contributes to the supply of the hip joint. Branches of the artery additionally anastomose with the lateral and medial femoral circum ex arteries from the deep femoral artery in the thigh, and with the inferior gluteal artery. Veins Inferior and superior gluteal veins follow the inferior and superior gluteal arteries into the pelvis where they join the pelvic plexus of veins. Peripherally, the veins anastomose with tremendous cial gluteal veins, which ultimately drain anteriorly into the femoral vein. Lymphatics Deep lymphatic vessels of the gluteal area accompany the blood vessels into the pelvic cavity and join with inside iliac nodes. Super cial lymphatics drain into the super cial inguinal nodes on the anterior aspect of the thigh. Structures enter and go away the top of the thigh by three routes: Posteriorly, the thigh is continuous with the gluteal region and the main construction passing between the 2 areas is the sciatic nerve. Anteriorly, the thigh communicates with the abdominal cavity via the aperture between the inguinal ligament and pelvic bone. Medially, constructions (including the obturator nerve and associated vessels) move between the thigh and pelvic cavity by way of the obturator canal. The thigh is split into three compartments (anterior, medial, and posterior) by intermuscular septa between the posterior aspect of the femur and the fascia lata (the thick layer of deep fascia that completely surrounds or invests the thigh;. Most of the large muscle tissue within the thigh insert into the proximal ends of the two bones of the leg (tibia and bula), and ex and extend the leg on the knee joint. The distal finish of the femur supplies origin for the gastrocnemius muscle tissue, which are predominantly in the posterior compartment of the leg and plantar ex the foot. Shaft and distal finish of femur the shaft of femur is bowed ahead and has an indirect course from the neck of the femur to the distal end. In the middle a half of the shaft, the femur has easy medial (posteromedial), lateral (posterolateral), and anterior surfaces and medial, lateral, and posterior borders. The medial and lateral borders are rounded, whereas the posterior border forms a broad roughened crest-the linea aspera. In proximal and distal areas of the femur, the linea aspera widens to type a further posterior surface. At the distal end of the femur, this posterior surface varieties the oor of the popliteal fossa and its margins, that are steady with the linea aspera above, form the medial and lateral supracondylar traces. The medial supracondylar line terminates at a distinguished tubercle (the adductor 288 tubercle) on the superior aspect of the medial condyle of the distal end.
Discount purim uk
In the context of autoimmune illness, a low C3 and/or C4 stage can be helpful measures of ongoing immune advanced formation. Autoantibody screening for a spread of specificities may be carried out relying on the medical context, using numerous methods during which a patents serum is examined for the presence of Ig that binds to purified antigens or to cells. Responses are decided by measuring serum levels of IgG particular to both T cell-dependent antigens (proteins or glycoproteins. Titers are mostly measured roughly 6 weeks post-vaccination, and low titers may warrant additional analysis for an underlying B cell immunodeficiency. Akt activation, in T cell activation, 156, 158f Alarmins, 60 Alemtuzumab, 413t Alkaline phosphatase, 537�538 Allelic exclusion, 195 Allergen(s), 437 nature of, 439 Allergic disease(s) genetic susceptibility to , 450�452, 451t in humans, pathogenesis and therapy of, 452�455 immunotherapy for, 455 Th2 cells and innate lymphoid cells in, 440 Allergic reactions basophils in IgE binding to , 442�443 mediators produced by, 442t morphology of, 441f properties of, 440�448, 441t eosinophils in, 448 mediators produced by, 442t morphology of, 441f properties of, 441t, 448 IgE-dependent, 448�450. Erythroblastosis fetalis, 393 Escherichia coli, 353t�354t E-selectin, in leukocyte recruitment, 41�42, 41t Exhaustion, 365 Exotoxins, 354 Extracellular bacteria, immunity to , 353t�354t, 354�357. Immuno-affinity chromatography, 533, 534f Immunoassays, quantitation of antigen by, 531�533, 532f Immunodeficiency(ies) acquired, 474�475, 474t affecting T or B lymphocytes, options of, 460t after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, 395 frequent variable, 465t congenital, 460�474 multisystem issues with, 473�474 Immunodeficiency illnesses acquired, 475�486. This concise, well-illustrated text provides an overview of the ideas of human pathology while emphasizing pathogenesis and the scientific features of disease. The key ideas and rules of pathology are offered in a condensed, at-a-glance format, making it the perfect pocket-sized reference for quick evaluate anytime! The processes that regulate haemopoiesis and the early phases of formation of purple cells (erythropoiesis), granulocytes and monocytes (myelopoiesis) and platelets (thrombopoiesis) are also discussed. Site of haemopoiesis In the primary few weeks of gestation the yolk sac is a transient site of haemopoiesis. These widespread precursors of endothelial and haemopoietic cells (haemangioblasts) are believed to seed the liver, spleen and bone marrow. From 6 weeks till 6�7 months of fetal life, the liver and spleen are the most important haemopoietic organs and continue to produce blood cells until about 2 weeks after birth (Table 1. During regular childhood and adult life the marrow is the only source of latest blood cells. The growing cells are located exterior the bone marrow sinuses; mature cells are launched into the sinus spaces, the marrow microcirculation and so into the general circulation. Even in these haemopoietic areas, approximately 50% of the marrow consists of fats. Haematoxylin and eosin stain; roughly 50% of the intertrabecular tissue is haemopoietic tissue and 50% is fats. Haemopoietic stem and progenitor cells Haemopoiesis begins with a pluripotential stem cell that may by asymmetric cell division selfrenew but also give rise to the separate cell lineages. These cells are capable of repopulate a bone marrow from which all stem cells have been eradicated by lethal irradiation or chemotherapy. Fetus 0�2 months (yolk sac) 2�7 months (liver, spleen) 5�9 months (bone marrow) Infants Adults Bone marrow (practically all bones) Vertebrae, ribs, sternum, cranium, sacrum and pelvis, proximal ends of femur in bone marrow. Many of the cells are dormant and in mice it has been estimated that they enter cell cycle roughly each 20 weeks. Cell differentiation happens from the stem cell by way of committed haemopoietic progenitors which are restricted in their developmental potential. The existence of the separate progenitor cells can be demonstrated by in vitro tradition strategies. Very early progenitors are assayed by tradition on bone marrow stroma as longterm culture initiating cells, whereas late progenitors are typically assayed in semisolid media. The bone marrow can be the first web site of origin of lymphocytes, which differentiate from a common lymphoid precursor. The spleen, lymph nodes and thymus are secondary sites of lymphocyte production (see Chapter 9). There is considerable amplification in the system: one stem cell is capable of producing about 106 mature blood cells after 20 cell divisions. With getting older, the variety of stem cells falls and the relative proportion giving rise to lymphoid rather than myeloid progenitors also falls.

Order purim in india
The characteristic purpuric rash accompanied by localized oedema and itching is often most distinguished on the buttocks and extensor surfaces of the decrease legs and elbows. It is often a selflimiting condition but occasional sufferers develop renal failure. In vitamin C deficiency faulty collagen may cause perifollicular petechiae, bruising and mucosal haemorrhage. Tranexamic acid and aminocaproic acid are useful anti fibrinolytic medication that may scale back bleeding ensuing from vascular problems or thrombocytopenia, however are comparatively contraindicated in the presence of haematuria as a end result of they may lead to clots obstructing the renal tract. Chapter 25: Bleeding disorders / 281 Thrombocytopenia Abnormal bleeding associated with thrombocytopenia or abnormal platelet function is characterized by spontaneous skin purpura. Failure of platelet manufacturing that is the commonest cause of thrombocytopenia and is often a half of a generalized bone marrow failure (Table 25. Selective megakaryocyte melancholy might end result from drug toxicity or viral infection. Failure of platelet manufacturing Selective megakaryocyte depression uncommon congenital defects (see text) drugs, chemical substances, viral infections Part of general bone marrow failure cytotoxic medication radiotherapy aplastic anaemia leukaemia myelodysplastic syndromes myelofibrosis marrow infiltration. Diagnosis of these causes of thrombocytopenia is made from the scientific historical past, peripheral blood rely, the blood film and bone marrow examination. Bone marrow suppression Predictable (doserelated) ionizing radiation, cytotoxic medication, ethanol Occasional chloramphenicol, cotrimoxazole, idoxuridine, penicillamine, organic arsenicals, benzene, and so forth. The highest incidence has been thought of to be in ladies aged 15�50 years, though some stories suggest an increasing incidence with age. Pathogenesis Platelet autoantibodies, normally IgG, result in the premature elimination of platelets from the circulation by macrophages of the reticuloendothelial system, especially the spleen. Total megakaryocyte mass and platelet turnover are increased in parallel to approximately 5 times normal. Clinical features the onset is usually insidious with petechial haemorrhage, easy bruising and, in girls, menorrhagia. These are orally lively or given by injection and act to increase platelet manufacturing. Treatment 6 7 As this is a continual illness the aim of treatment ought to be to keep a platelet depend above the extent at which spontaneous bruising or bleeding occurs with the minimal of intervention. Prednisolone 1 mg/kg/day is the standard preliminary remedy in adults and the dosage is steadily reduced after 10�14 days. In poor responders the dosage is reduced extra slowly however various immunosuppression or splenectomy is taken into account. The mechanism of motion may be blockage of Fc receptors on macrophages or modification of autoantibody production. Trials of their use as initial therapy in combination with corticosteroids are in progress. Increased reticulin and fibrosis in the bone marrow could happen with extended therapy but are reversible on stopping the remedy. Other therapies which will elicit a remission embrace danazol (an androgen which can cause virilization in women) and intravenous antiD immunoglobulin. Helicobacter pylori infection ought to be treated as there are some reports that this will improve the platelet depend, significantly in countries where the incidence of the infection is widespread. Platelet transfusions Platelet concentrates are beneficial in sufferers with acute lifethreatening bleeding however their profit will solely final for a couple of hours. In approximately 75% of sufferers the episode follows vaccination or an infection similar to chickenpox or infectious mononucleosis. Spontaneous remissions are traditional however in 5�10% of cases the illness turns into chronic, lasting more than 6 months. If the platelet rely is over 30 � 109/L no therapy is important until the bleeding is extreme. Infections It appears doubtless that the thrombocytopenia related to many viral and protozoal infections is immunemediated. Druginduced immune thrombocytopenia An immunological mechanism has been demonstrated as the reason for many druginduced thrombocytopenias. Quinine (including that in tonic water), quinidine and heparin are significantly widespread causes (Table 25. The platelet rely is usually less than 10 � 109/L, and the bone marrow shows regular or elevated numbers of megakaryocytes. Drugdependent antibodies in opposition to platelets may be demonstrated within the sera of some patients.