Cytotec dosages: 200 mcg, 100 mcg
Cytotec packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills

Purchase 100mcg cytotec otc
Pasqualetti P, Festucci V, Collacciani A, Casale R: the natural history of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Morra E, Cesana C, Klersy C, et al: Clinical traits and components predicting evolution of asymptomatic IgM monoclonal gammopathies and IgM-related issues. Montoto S, Rozman K, Rosinol L, et al: Malignant transformation in IgM monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Van De Donk N, De Weerdt O, Eureling M, et al: Malignant transformation of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance: Cumulative incidence and prognostic elements. Cesana C, Klersy C, Barbarano L, et al: Prognostic elements for malignant transformation in monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and smoldering a quantity of myeloma. Zhan F, Barlogie B, Arzoumanian V, et al: Gene-expression signature of benign monoclonal gammopathy evident in a number of myeloma is linked to good prognosis. Bacher U, Haferlach T, Kern W, et al: Correlation of cytomorphology, immunophenotyping, and interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization in 381 sufferers with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and 301 sufferers with plasma cell myeloma. Yi Q, Osterborg A, Bergenbrant S, et al: Idiotype-reactive T-cell subsets and tumor load in monoclonal gammopathies. Corso A, Castelli G, Pagnucco G, et al: Bone marrow T-cell subsets in sufferers with monoclonal gammopathies: Correlation with clinical stage and illness. Miguel-Garcia A, Matutes E, Tarin F, et al: Circulating Ki-67 constructive lymphocytes in multiple myeloma and benign monoclonal gammopathy. Billadeau D, Van Ness B, Kimlinger T, et al: Clonal circulation cells are frequent in plasma cell proliferative problems: A comparability of monoclonal gammopathy, smoldering myeloma, and active myeloma. Sawanoborj M, Suzuki K, Nakagawa Y, et al: Natural killer cell frequency and serum cytokine levels in monoclonal gammopathies: Correlation of bone marrow granular lymphocytes to prognosis. French M, Fench P, Remy F, et al: Plasma cell proliferation in monoclonal gammopathy: Relations with other biologic variables-Diagnostic and prognostic significance. Amiel A, Kirgner I, Gaber E, et al: Replication sample in most cancers: Asynchronous replication in multiple myeloma and in monoclonal gammopathy. Yasuda N, Kanoh T, Uchino H: J chain synthesis in human myeloma cells: Light and electron microscopic studies. Sezer O, Heider U, Zavrski I, Possinger K: Differentiation of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and a number of myeloma using flow cytometric characteristics of plasma cells. Bellaiche L, Laredo J-D, Liot� F, et al: Magnetic resonance look of monoclonal gammopathies of unknown significance and multiple myeloma. Bataille R, Chappard D, Basle M: Quantifiable extra of bone resorption in monoclonal gammopathy is an early symptom of malignancy: A potential examine of 87 bone biopsies. Greco C, Ameglio F, Alvino S, et al: Selection of patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance is obligatory for a reliable use of interleukin-6 and different nonspecific a quantity of myeloma serum markers. Cozzolino F, Torcia M, Aldinucci D, et al: Production of interleukin-1 by bone marrow myeloma cells. Diamond T, Levy S, Smith A, et al: Non-invasive markers of bone turnover and plasma cytokines differ in osteoporotic patients with multiple myeloma and monoclonal gammopathies of undetermined significance. It originates in most, maybe all, circumstances from an antecedent monoclonal gammopathy (essential monoclonal gammopathy) that progresses by clonal evolution (acquisition of additional mutations) to a malignant B-cell malignancy, typically myeloma, at a rate of 1 p.c per yr. Myeloma cells accumulate in the marrow microenvironment the place contact with extracellular matrix and interplay with marrow accessory cells, such as osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and stromal cells, evokes cell growth and cell-survival signals, and contributes to resistance to therapy. Myeloma cells show a complex genomic phenotype, with chromosomal translocations and small copy quantity variations that affect patient prognosis. Patients with myeloma have signs ensuing from marrow infiltration (anemia), bone destruction (bone pain, pathologic fractures), excessive immunoglobulin production and deposition (renal failure and amyloidosis-related symptoms), and immunosuppression. Clinical manifestations of myeloma vary on account of the heterogeneous biology, spanning the complete spectrum from indolent to extremely aggressive disease with extramedullary features. Diagnostic workup of myeloma should embody serum protein electrophoresis along with immunoglobulin immunofixation, serum-free light-chain assay, a 24-hour urine collection to quantitate urinary protein, primary blood metabolic panel including blood counts and renal operate, and marrow aspirate or biopsy with fluorescence in situ hybridization and cytogenetic studies. Radiographic bone survey is used to detect osteopenia and bone lesions or impending fractures. The most typical staging system for myeloma is the International Staging System, primarily based on two parameters, serum 2-microglobulin (2M) and albumin; three phases are defined and correlate with patient end result. Serum levels of 2M, C-reactive protein, number of circulating plasma cells and their labeling-index are associated to affected person prognosis. Consolidation and upkeep regimens based mostly on lenalidomide as single agent or together with bortezomib have been evaluated to prolong the duration of full remission following autologous stem cell transplant. Myeloma derives from cells with plasma cell morphologic features, capable of producing immunoglobulin molecules (Chap.
Syndromes
- Echocardiogram to look at the heart
- Inability to speak
- Thymus
- Decreased language ability (aphasia)
- Breathing difficulty
- Open the airway. Lift up the chin with one hand. At the same time, tilt the head by pushing down on the forehead with the other hand.
- Chronic nerve problems caused by poor posture, which result in numbness or tingling in your arms or hands.
- Angioedema does not respond to treatment
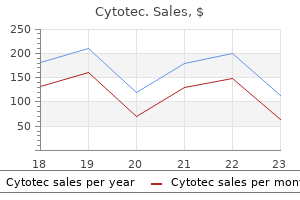
Order cytotec american express
Notably, there have been no instances of treatmentrelated-myeloid neoplasms occurring earlier than illness relapse. Similarly, cladribine and cladribine plus cyclophosphamide have been additionally combined with rituximab and resulted in predictable efficacy and toxicity. The bleeding diathesis observed with ibrutinib is presumably brought on by a collagenmediated platelet aggregation defect. The pathophysiologic reason for increased threat of atrial fibrillation with ibrutinib is uncertain. Ibrutinib therapy additionally ends in a progressive decline in the incidence of infectious problems with ongoing remedy, primarily because of illness control. Moreover, enhancements are additionally noticed in stress, depressive signs, fatigue, and quality-of-life in sufferers treated with ibrutinib. Therefore, we presently suggest that ibrutinib be continued in responding patients until illness development or unacceptable toxicity. However, this continual publicity to kinase inhibitors might outcome in the emergence of resistant malignant cell clones, though this has been fairly uncommon. Ibrutinib is being mixed with various different brokers to enhance the depth of response and outcomes. Multiple trials are ongoing with ibrutinib within the frontline setting and in comparison to chemoimmunotherapy. Therapy was usually welltolerated with the most commonly observed grade 3 or larger antagonistic events being pneumonia (20 percent), neutropenic fever (11 percent), and diarrhea (6 percent). Idelalisib Lenalidomide Lenalidomide is an immunomodulatory analogue of thalidomide and is approved for the treatment of a quantity of myeloma and myelodysplastic syndrome. Patients can even experience tumor flare and tumor lysis, particularly initially of remedy. Care should be taken to minimize these reactions with the early use of steroids and aggressive hydration and uricosuric brokers. Combination of lenalidomide with monoclonal antibodies has also resulted in improved sustained responses. Early efforts with the first-generation compound navitoclax, demonstrated single-agent exercise, but additionally resulted in profound thrombocytopenia as a outcome of off-target effects on Bcl-xl expressed in platelets. Venetoclax is considerably more potent and more particular to Bcl-2 with restricted off-target effects. Therapy with venetoclax has been complicated by fulminant tumor lysis syndrome, particularly in patients with a excessive burden of disease that has significantly slowed down medical development of this agent. Therapy is sophisticated by hypogammaglobulinemia, cytokine launch and neurologic signs. It could be an efficient option for ameliorating refractory autoimmune hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia for which medical administration has been unsuccessful. Splenic irradiation can be utilized in sufferers with symptomatic splenomegaly, but its efficacy is limited and short-lived with vital and typically extended myelosuppression. However, this modality can be utilized for the occasional patient who becomes symptomatic from hyperleukocytosis. Leukapheresis has been used in the past for patients with refractory illness as a therapeutic choice, however it ends in modest and transient benefits. This includes performing an in depth history for any disease-related symptoms, physical examination for any palpable lymphadenopathy, and laboratory research to evaluate for persistent cytopenias or leukocytosis. Formal response criteria for illness evaluation had been revised with the advent of kinase inhibitors. We advocate ready till count recovery or three to 6 months after chemotherapy to repeat a marrow biopsy for persistent cytopenias. Occasionally, patients may have no evidence of illness on flow cytometry of the aspirate or on the biopsy specimen but could have nodular lymphoid aggregates. For patients older than age sixty five years and people with multiple comorbid circumstances or renal insufficiency, we suggest remedy with either obinutuzumab or ofatumumab with chlorambucil.
Buy cytotec 200mcg mastercard
Andre P, et al: P2Y12 regulates platelet adhesion/activation, thrombus progress, and thrombus stability in injured arteries. Fontana P, et al: Adenosine diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation is related to P2Y12 gene sequence variations in wholesome topics. Leon C, et al: Defective platelet aggregation and elevated resistance to thrombosis in purinergic P2Y(1) receptor-null mice. Oury C, et al: Does the P(2X1del) variant lacking 17 amino acids in its extracellular area characterize a relevant practical ion channel in platelets Oury C, et al: P2X(1)-mediated activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 contributes to platelet secretion and aggregation induced by collagen. Vial C, et al: A examine of P2X1 receptor function in murine megakaryocytes and human platelets reveals synergy with P2Y receptors. Oury C, et al: Overexpression of the platelet P2X1 ion channel in transgenic mice generates a novel prothrombotic phenotype. Yang J, et al: Loss of signaling by way of the G protein, Gz, ends in irregular platelet activation and altered responses to psychoactive medication. Redundancy and specificity within the regulation of adenylyl cyclase and different effectors. Freeman K, et al: Genetic polymorphism of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor is related to increased platelet aggregation, baroreceptor sensitivity, and salt excretion in normotensive humans. Sibbing D, et al: Platelet operate in clopidogrel-treated patients with acute coronary syndrome. Svensson J, Hamberg M, Samuelsson B: On the formation and effects of thromboxane A2 in human platelets. Rocca B, et al: Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is induced during human megakaryopoiesis and characterizes newly shaped platelets. Ushikubi F, et al: Purification of the thromboxane A2/prostaglandin H2 receptor from human blood platelets. Gabbeta J, et al: Platelet signal transduction defect with Ga subunit dysfunction and diminished Gaq in a affected person with abnormal platelet responses. Djellas Y, et al: Identification of Galpha13 as one of the G-proteins that couple to human platelet thromboxane A2 receptors. Nakahata N, et al: Gq/11 communicates with thromboxane A2 receptors in human astrocytoma cells, rabbit astrocytes and human platelets. Ushikubi F, Nakamura K, Narumiya S: Functional reconstitution of platelet thromboxane A2 receptors with Gq and Gi2 in phospholipid vesicles. Klages B, et al: Activation of G12/G13 leads to form change and Rho/Rhokinase-mediated myosin mild chain phosphorylation in mouse platelets. Maugeri N, et al: Polymorphonuclear leukocyte-platelet interplay: Role of Pselectin in thromboxane B2 and leukotriene C4 cooperative synthesis. Zhang C, et al: High-resolution crystal structure of human protease-activated receptor 1. Ishihara H, et al: Antibodies to protease-activated receptor 3 inhibit activation of mouse platelets by thrombin. Andrade-Gordon P, et al: Design, synthesis, and organic characterization of a peptide-mimetic antagonist for a tethered-ligand receptor. Berri F, et al: Switch from protective to adverse irritation throughout influenza: Viral determinants and hemostasis are caught as culprits. Celikel R, et al: Modulation of alpha-thrombin perform by distinct interactions with platelet glycoprotein Ibalpha. Honda Z, et al: Cloning by functional expression of platelet-activating issue receptor from guinea-pig lung. Nakamura M, et al: Molecular cloning and expression of platelet-activating issue receptor from human leukocytes. Chao W, et al: Protein tyrosine phosphorylation and regulation of the receptor for platelet-activating factor in rat Kupffer cells. Sano T, et al: Multiple mechanisms linked to platelet activation end in lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate technology in blood. Umezu-Goto M, et al: Autotaxin has lysophospholipase D exercise resulting in tumor cell growth and motility by lysophosphatidic acid manufacturing. Leblanc R, et al: Interaction of platelet-derived autotaxin with tumor integrin alphaVbeta3 controls metastasis of breast cancer cells to bone.
Buy cytotec with a visa
Patients with visceral involvement that includes liver, spleen, pleura, and lung have a median survival of less than 1 12 months. Note the nuclear swirls and the light microscopic appearance of the S�zary cell nucleus. Without careful inspection in cases of lymphocytosis, S�zary cells can be mistaken for small lymphocytes as seen in persistent lymphocytic leukemia. Blood lymphocytes from a affected person with mycosis fungoides and disseminated illness involving marrow and blood. The latter have the hanging cerebriform nuclear abnormalities characteristic of S�zary cells. It often presents as crops of recurrent pruritic or painful erythematous papules or nodules, which ulcerate and heal spontaneously. Therapeutic choices could also be difficult and heavily depend on the stage at presentation. They are limited to momentary short-term use because of suppression of collagen synthesis (skin atrophy), striae formation, pores and skin fragility, and secondary infections. Topical steroids are rarely used as monotherapy, however may be efficient as an additional modality for symptomatic relieve of pruritus. Topical Tacrolimus (Protopic) Topical tacrolimus has been accredited for use in atopic dermatitis. Disadvantages include the inconvenience of every day software to large areas of pores and skin, allergic reactions in up to half of cases,eighty five the potential for growth of skin cancer,86 and the lack to remedy the illness. Therapy is discontinued after three years or when cutaneous lesions disappear fully. Monitoring consists of biweekly complete blood counts to establish marrow suppression. Carmustine causes irreversible skin thinning, telangiectasias, and hyperpigmentation. Long-term unwanted effects embrace an increased incidence of pores and skin cancers and melanoma. Red-light irradiation is secure and penetrates deep within the tissue, permitting for treatment of thick tumors. Photodynamic remedy is very helpful in sufferers with restricted skin area involved by few tumors. The major drawback with the remedy is that the ache induced throughout irradiation limits its use for bigger areas. It delivers a uniform dose from the floor to a specific depth, after which the dose falls off rapidly, sparing deeper regular tissues. It is usually delivered to penetrate solely into the dermis, systemic results are minimal, and the entire remission fee is eighty p.c. The relapse fee depends on the stage of the disease, and the relapse often is short lived (may be as brief as 2 to 3 weeks) in sufferers with erythroderma or numerous tumors. In the past, the treatment routine was four Gy per week to a total dose of 36 Gy in eight to 9 weeks. However, low-dose electron beam remedy has been proven to be practically as effective, eliminating the standard unwanted facet effects, similar to alopecia, pores and skin atrophy, destruction of skin adnexa, dermatitis, and elevated risk of cutaneous malignancy. Up to three programs of electron beam remedy may be safely administered when utilized in a highly fractionated fashion (1 Gy per dose). It is a first-line systemic agent for sufferers without contraindications to retinoids. All patients on bexarotene rapidly develop central hypothyroidism and hyperlipidemia (most considerably hypertriglyceridemia), requiring coadministration of thyroid dietary supplements and lipid-lowering agents. Other uncommon adverse occasions include complications, possibly a result of pseudotumor cerebri, leucopenia, and pruritus. The majority of unwanted effects are laboratory findings and dose-dependent; bexarotene is usually properly tolerated by the patients. Standard procedures for management of patients on bexarotene therapy are reviewed. Bexarotene and different retinoids are labeled being pregnant Category X, and should not be given to a pregnant lady or a girl who intends to become pregnant.
Cytotec 200mcg generic
Hochhaus A, Weisser A, LaRosee P, et al: Detection and quantification of residual illness in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Sobrinho-Sim�es M, Wilczek V, Score J, et al: In search of the unique leukemic clone in persistent myeloid leukemia paients in full molecular remission after stem cell transplantation or imatinib. Wodarz D: Stem cell regulation and the event of blast disaster in chronic myeloid leukemia: Implications for the result of Imatinib remedy and discontinuation. Brazma D, Grace C, Howard J, et al: Genomic profile of chronic myelogenous leukemia: Imbalances related to illness development. Swolin B, Weinfeld A, Westin J, et al: Karyotypic evolution in Ph-positive continual myeloid leukemia in relation to management and disease development. Yamaguchi H, Inokuchi K, Sakuma Y, Dan K: Mutation of p51/p63 gene is related to blast crisis in persistent myelogenous leukemia. Griesshammer M, Heinze B, Bangerter M, et al: Karyotype abnormalities and their medical significance in blast disaster of continual myeloid leukemia. Spencer A, Vulliamy T, Kaeda J, et al: Clonal instability preceding lymphoid blastic transformation of chronic myeloid leukemia. Okabe M, Matsushima S: Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia: Molecular analysis of bcr and abl genes and remodeling genes. Ahuja H, Bar-Eli M, Arlin Z, et al: the spectrum of molecular alterations in the evolution of continual myelocytic leukemia. Kelman Z, Prokocimer M, Peller S, et al: Rearrangements within the p53 gene in Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myelogenous leukemia. Mashal R, Shtalrid M, Talpaz M, et al: Rearrangement and expression of p53 in the continual part and blast disaster of continual myelocytic leukemia. Malinen T, Palotie A, Pakkala S, et al: Acceleration of persistent myeloid leukemia correlates with calcitonin gene methylation. Towatari M, Adachi K, Kato H, Saito H: Absence of the human retinoblastoma gene product in the megakaryoblastic disaster of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Mori N, Takeuchi S, Tasaka T, et al: Absence of microsatellite instability during the development of persistent myelocytic leukemia. Daheron L, Salmeron S, Patri S, et al: Identification of several genes differentially expressed during development of continual myelogenous leukemia. Mori N, Morosetti R, Loe S, et al: Allelotype evaluation within the evolution of persistent myelocytic leukemia. Matsuo T, Tomonaga M, Kuriyama K, et al: Prognostic significance of the morphological dysplastic adjustments in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Specchia G, Palumbo G, Pastore D, et al: Extramedullary blast crisis in chronic myeloid leukemia. Inveradi D, Lazzarino M, Morra E, et al: Extramedullary illness in Ph-positive persistent myelogenous leukemia: Frequency, medical options, prognostic significance. Jacknow J, Fizzera G, Gajl-Peczalska K, et al: Extramedullary presentation of the blast crisis of persistent myelogenous leukemia. Terjanian T, Kantarjian H, Keating M, et al: Clinical and prognostic options of sufferers with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia and extramedullary disease. Asarro S, Sato N, Ueshima Y, et al: Localized blastoma preceding blastic transformation in Ph1-positive persistent myelogenous leukemia. Ohyashiki K, Ito H: Characterization of extramedullary tumors in a case of Phpositive chronic myelogenous leukemia. Sun T, Susin M, Koduru P, et al: Extramedullary blast crisis in continual myelogenous leukemia. Ohyashiki J, Ohyashiki K, Shimizu H, et al: Testicular tumor as the primary manifestation of B-lymphoid blastic disaster in a case of Ph-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia. Bettelheim P, Lutz D, Majdic O, et al: Cell lineage heterogeneity in blast crisis of persistent myeloid leukaemia. Nair C, Chopra M, Shinde S, et al: Immunophenotype and ultrastructural research in blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia. Ekblom M, Borgstrom G, von Willebrand E, et al: Erythroid blast crisis in continual myelogenous leukemia. Lingg G, Schmalzl F, Breton-Gorius J, et al: Megakaryoblastic micro-megakaryocytic disaster in continual myeloid leukemia.
Protease (Bromelain). Cytotec.
- Preventing muscle soreness after exercise.
- Arthritis (osteoarthritis) when used in combination with trypsin and rutin.
- How does Bromelain work?
- Dosing considerations for Bromelain.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What other names is Bromelain known by?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- What is Bromelain?
- Knee pain, severe burns, inflammation, reducing swelling after surgery or injury, improving antibiotic absorption, hayfever, preventing cancer, shortening of labor, making it easier to get rid of fats, ulcerative colitis, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96862
Order cytotec 100mcg with visa
Klein G: Lymphoma growth in mice and people: Diversity of initiation is followed by convergent cytogenetic evolution. Klein G: Specific chromosomal translocations and the genesis of B-cell-derived tumors in mice and men. Dotti G, Fiocchi R, Motta T, et al: Primary effusion lymphoma after coronary heart transplantation: A new entity associated with human herpesvirus-8. Laurent C, Meggetto F, Brousset P: Human herpesvirus 8 infections in sufferers with immunodeficiencies. Okan V, Yilmaz M, Bayram A, et al: Prevalence of hepatitis B and C viruses in patients with lymphoproliferative problems. Inokuchi M, Ito T, Uchikoshi M, et al: Infection of B cells with hepatitis C virus for the event of lymphoproliferative problems in sufferers with continual hepatitis C. Yakushijin Y, Kodama T, Takaoka I, et al: Absence of chlamydial an infection in Japanese sufferers with ocular adnexal lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Cunningham-Rundles C, Bodian C: Common variable immunodeficiency: Clinical and immunological options of 248 patients. Kaneko H, Inoue R, Fukao T, et al: Two Japanese siblings with Bloom syndrome gene mutation and B-cell lymphoma. Capello D, Rossi D, Gaidano G: Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders: Molecular basis of illness histogenesis and pathogenesis. Dolcetti R: B lymphocytes and Epstein-Barr virus: the lesson of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Ji J, Shu X, Li X, et al: Cancer risk in hospitalized sarcoidosis sufferers: A follow-up study in Sweden. Histopathology, immunophenotype, and affiliation with Epstein-Barr virus as demonstrated by in situ nucleic acid hybridization. Paul T, Challa S, Tandon A, et al: Primary central nervous system lymphomas: Indian expertise, and review of literature. Kozakova D, Machalekova K, Brtko P, et al: Primary B-cell pituitary lymphoma of the Burkitt type: Case report of the rare clinic entity with typical medical presentation. Riemens A, Bromberg J, Touitou V, et al: Treatment strategies in primary vitreoretinal lymphoma: A 17-center European collaborative study. Oprea C, Cainap C, Azoulay R, et al: Primary diffuse massive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma of the paranasal sinuses: A report of 14 instances. Zhao J, Han B, Shen T, et al: Primary cutaneous diffuse massive B-cell lymphoma (leg type) after renal allograft: Case report and review of the literature. Tabatabai A, Hashemi M, Ahmadinejad M, et al: Primary chest wall lymphoma with no history of tuberculous pyothorax: Diagnosis and remedy. Ikeda H, Nakamura S, Nishimaki H, et al: Primary lymphoma of the guts: Case report and literature evaluate. Legault S, Couture C, Bourgault C, et al: Primary cardiac Burkitt-like lymphoma of the right atrium. Nakamura S, Matsumoto T: Gastrointestinal lymphoma: Recent advances in diagnosis and treatment. Psyrri A, Papageorgiou S, Economopoulos T: Primary extranodal lymphomas of abdomen: Clinical presentation, diagnostic pitfalls and management. Doi H, Horiike N, Hiraoka A, et al: Primary hepatic marginal zone B cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue sort: Case report and evaluate of the literature. Sata N, Kurogochi A, Endo K, et al: Follicular lymphoma of the pancreas: A case report and proposed new strategies for prognosis and surgery of benign or low-grade malignant lesions of the pinnacle of the pancreas. Pectasides D, Iacovidou I, Psyrri A, et al: Primary ovarian lymphoma: Report of two cases and review of the literature. Hamadani M, Kharfan-Dabaja M, Kamble R, et al: Marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the uterus: A case report and evaluation of the literature. Brancato T, Alvaro R, Paulis G, et al: Primary lymphoma of the kidney: Case report and evaluation of literature. Kubota Y, Kawai A, Tsuchiya T, et al: Bilateral main malignant lymphoma of the ureter. Hughes M, Morrison A, Jackson R: Primary bladder lymphoma: Management and consequence of 12 patients with a evaluate of the literature. Terzic T, Radojevic S, Cemerikic-Martinovic V, et al: Primary non-Hodgkin lymphoma of urinary bladder with nine years later renal involvement and absence of systemic lymphoma: A case report.
Cheap cytotec generic
This regimen was characterized by extreme marrow toxicity, and more than 10 percent of sufferers died of regimen-related toxicity. Other intensive regimens have additionally been used, with 4-year overall survival of 70 p.c, but with death in eleven percent from regimen-related toxicity. In one sequence, the most common symptom was headache, adopted by reminiscence loss, ataxia, and seizure. Small retrospective series report that whole-brain radiation remedy can lead to improved survival,149 however roughly one-third of these patients had detectable leukoencephalopathy on followup. A large retrospective study discovered that treatment with whole-brain radiation remedy and/or chemotherapy was related to a decreased risk of demise,151 but this evaluation is confounded by ignorance on performance standing. Small numbers of sufferers have been treated with multiple cycles of high-dose methotrexate with leucovorin rescue, without radiation therapy, with prolonged survival and no cognitive dysfunction,158,159 and this can be a reasonable choice in patients with good efficiency status. Other widespread websites of involvement have been the gastrointestinal monitor, the lymph nodes and skin, among different sites. The pathology reveals a monomorphic diffuse lymphoid infiltrate with cells resembling plasmablasts. The cells have a high proliferative fee with a Ki-67 typically exceeding ninety %, and are positive for plasma cell markers. Case reviews of particular person sufferers recommend that bortezomib might have exercise in these sufferers, and this should be explored in future clinical trials. A stable variant of major effusion lymphoma presents with out effusion, but with lymph node, gastrointestinal, skin, or liver involvement has been reported. A high index of suspicion for lymphoma is needed in order that appropriate samples are despatched to Hematopathology for evaluation. Approximately 50 % of patients with primary effusion lymphoma achieve a complete response, but relapse within the next few months is common, and the median survival is roughly 6 months, with most deaths a result of progressive lymphoma. The use of rituximab was considerably related to improved general survival (hazard ratio zero. Patients with a low score (0 to 1 points) had a 5-year total survival of 96 percent; patients with a low intermediate rating (2 to three points) had a 5-year general survival of 82 %; patients with a high intermediate score (4 to 5 points) had a 5-year general survival of sixty four p.c, and sufferers with excessive danger (6 to eight points) had an general 5-year survival of 33 p.c. This scale supplied higher danger stratification than the original International Prognostic Index, which was developed in the prerituximab period. The total survival was 76 % at 5 years, with treatment-related mortality of 10 %. The threat for nonrelapse mortality is in the 5 to eight percent vary and the general survival at 3 to four years after transplantation is approximately 50 percent. The main explanation for demise was relapse and the most important predictor of end result in each groups was disease status at time of transplantation. Others have also discovered that protease inhibitors may exacerbate chemotherapy-induced neutropenia,203 although that is controversial. Zidovudine causes marrow suppression, and must be prevented in sufferers receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy. Didanosine and stavudine (older, sometimes used agents) cause peripheral neuropathy, and their use should be reconsidered in patients who will receive potentially neurotoxic chemotherapy. Atazanavir, a commonly prescribed protease inhibitor, causes unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia similar to Gilbert syndrome and might complicate the administration of some chemotherapy brokers. Symptoms at presentation included fever, lymphadenopathy, and splenomegaly in 98 to one hundred pc, pulmonary symptoms in 60 percent, and edema in 40 % of sufferers. A single-institution research of 113 sufferers with Castleman disease214 additionally reported that roughly half of the sufferers had a prior prognosis of Kaposi sarcoma. During a Castleman illness flare, sufferers may rapidly develop cytopenias: half the patients in this sequence had a hemoglobin of less than 8 g/dL and 29 % had a platelet count of lower than one hundred fifty,000/L. Castleman disease is uncommon, and therapy recommendations are largely primarily based on case collection and small medical trials. Prospective studies213,218,219 reveal that 375 mg/m2 of rituximab administered intravenously weekly for four doses resulted in rapid symptomatic improvement, and ninety percent of patients achieved a response that lasted for greater than 6 months. The median progression-free interval was 6 months and the most important toxicity was marrow suppression.
Buy cytotec 100mcg
Other inherited syndromes with hemophagocytosis lymphohistiocytosis: Ch�diak-Higashi, X-linked lymphoproliferative, Gracelli29 C. Aging90�92 cells, dedicated to the monocyte-macrophage lineage, can endure malignant transformation (Chaps. Several unusual forms of histiocytosis are serious systemic ailments that may masquerade as malignant illness. Familial and sporadic hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, infection-induced hemophagocytic syndromes, and sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy are amongst such disorders (Chap. Infectious hemophagocytic histiocytosis caused by Epstein-Barr virus could also be a hybrid illness due to the affiliation with an underlying monoclonal or oligoclonal proliferation of virus-infected lymphocytes. The hanging activation of macrophages and the resulting cytokine elaboration and organ pathology seen in some sufferers with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, referred to as the "macrophage-activation syndrome," is closely associated to different kinds of hemophagocytic syndromes (Chap. Pediatric rheumatologists check with the hemophagocytic syndrome in patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis because the "macrophage activation syndrome," but the scientific expression is intently analogous to other acquired hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytic syndromes. Tumors of histiocytes (or dendritic cells) are rare, but can be categorized into several groups with a combination of morphologic and immunophenotypic markers (Chap. In these situations the abnormality is usually shared by other leukocytes, as in persistent granulomatous disease, which ends from a defect in oxygen-dependent microbial killing. In Ch�diakHigashi illness, defective macrophages result from an abnormality of their cell and granule membranes (Chap. An indomethacinsensitive monocyte-killing defect in kids is associated with a predisposition to atypical mycobacterial illness. Also, inherited or enzyme deficiencies in macrophages may find yourself in accumulation of undegraded macromolecules, resulting in numerous kinds of storage illnesses. A traditional instance is Gaucher disease, a dysfunction that outcomes from an inherited deficiency of the enzyme glucocerebrosidase, during which tissue damage outcomes from the engorgement of macrophages with the enzyme substrate. Recombinant glucocerebrosidase, which enters macrophage lysosomes by endocytosis, can ameliorate this macrophagic disease (Chap. Monocyte dysfunction happens after extreme trauma, sepsis, in different critically ill sufferers, and in sufferers with metastatic cancer. Tobacco smoking and marijuana smoking can end result in impairment of alveolar macrophage perform. In a number of ailments, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Kawasaki illness, Whipple illness, and malakoplakia, specific abnormalities of monocyte perform play a significant role in the immune impairment in each dysfunction. Neutrophils, endothelial cells, and different cell varieties can substitute, in part, for some monocyte capabilities. Monocytes have antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, and antiparasitic capabilities. They are efficient phagocytes which might be concerned within the ingestion and inactivation of microbes, corresponding to mycobacteria, Listeria, Brucella, trypanosomes, and different granuloma-producing organisms. Macrophages can serve as a reservoir for the human immunodeficiency virus and are the principal locus for the virus within the mind and in neural tissue. Deficiency in a selected subset of macrophages, the osteoclasts, ends in osteopetrosis, an imbalance in bone metabolism that favors accretion. Osteoclasts usually play a key role within the carefully regulated means of bone resorption and accretion, mediating the former process. Monocyte derivatives are, thereby, involved in the development of osteoporosis and different metabolic bone illnesses by which the steadiness tips towards resorption. Bisphosphonates can inhibit osteoclast action by interfering with its operate of bone resorption and by inhibiting the mevalonate pathway to geranylgeranyl diphosphate, which prevents the transformation of monocytes to osteoclasts. Thus, the deleterious clinical manifestations of macrophages are being subdued by making the monocyte a goal of remedy, in this case the prevention and amelioration of postmenopausal osteoporosis, tumor-induced bone lysis, and Paget disease, as well as of others. Macrophages and their derivatives, monocyte-derived dendritic cells, course of and present antigens and play a role in immune regulation. In advanced techniques, corresponding to that of antibody production, abnormal macrophages would possibly result in defects in humoral immunity. Activated monocytes secrete greater than 50 chemical mediators or monokines, which, amongst other things, play a vital position in mobile immunity and inflammation. A deficiency or impairment of monocytes has the potential of influencing a number of capabilities and methods, as a outcome of monocytes are such necessary sources of inflammatory cytokines (Chap. In distinction, the unregulated activation of monocytes can lead to deleterious cytokine elaboration. Monocytopenia and decreased monocyte entry into inflammatory websites happen after glucocorticoid administration.

Purchase cytotec 200 mcg on-line
Historically, the 10-year threat of pituitary involvement has been reported as 24 p.c. T2-weighted magnetic resonance image of the brain of a patient with Langerhans cells histiocytosis showing hyperintense adjustments of the cerebellar white matter. Women or males with genital lesions could additionally be thought to have a sexually transmitted illness or other infection. Oral lesions mimic different ulcerative conditions, gingival infections, or dental caries. Lytic bone lesions are sometimes thought to be evidence of a malignancy corresponding to neuroblastoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, or Ewing sarcoma. An enlarged thymus or mediastinal lymph nodes could cause respiratory misery and wheezing just like bronchial asthma. Other approaches with reported efficacy include oral methotrexate (20 mg/m2 weekly)69 or oral thalidomide (50 to 200 mg daily). Single Skull Lesions of the Frontal, Parietal, or Occipital Regions, or Single Lesions of Any Other Bone Curettage or curettage plus injection of methylprednisolone may be used. After the first 6 weeks, oral prednisone is given for 5 days at forty mg/m2 each three weeks with the vinblastine intravenous. Patients with suboptimal responses by 6 weeks are given an extra 6 weeks of weekly intravenous vinblastine. Both shorter (<6 months) treatment methods and treatment with only a single agent. A 37 percent reactivation price with a two-drug regimen has been reported, versus 50 to 80 % with only surgical procedure or single-drug remedies. Central Nervous System Treatment of mass lesions, including enlargement of the hypothalamic�pituitary axis, parenchymal mass lesions, and leptomeningeal involvement, with cladribine has been efficient. Doses of cladribine ranged from 5 to 13 mg/m2 given intravenously at various frequencies. Strategies include oral dexamethasone, intravenous cladribine, oral all-trans retinoic acid, intravenous immunoglobulin, and intravenous cytarabine. Recurrent, Refractory, or Progressive Childhood Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis Recurrent "Low-Risk" Organ Involvement the optimal therapy for patients with relapsed or recurrent illness has not been determined. Patients with recurrent bone illness who reoccur greater than 6 months after stopping vinblastine and prednisone can profit from treatment with a "reinduction" of intravenous vinblastine, weekly, and day by day oral prednisone for 6 weeks. Three approaches (1) intravenous cladribine, (2) intravenous vincristine and intravenous cytarabine, and (3) intravenous clofarabine are efficient regimens for patients with recurrent bone illness. However, dose-limiting toxicities and extraordinary value restrict the overall usefulness of thalidomide. Treatment with high-dose cladribine (9 mg/m2 per day) coupled with cytarabine (1 g/m2 per day) for five days for a minimum of 2 months resulted in increased total survival and remedy in beforehand refractory sufferers. Reduced-intensity conditioning regimens are healing and associated with much less toxicity and improved survival. Similarly, surgical resection or radiotherapy of groin or genital lesions is contraindicated as chemotherapy can heal skin lesions. Children with low-risk organ involvement (skin, bones, lymph nodes, or pituitary gland) handled for 6 months have a 24 p.c chance of creating long-term sequelae. Patients handled earlier than 2000 with multisystem involvement had a seventy one % incidence of long-term issues. These problems embrace vertebral collapse or instability of the spine which will result in scoliosis, and facial or limb asymmetry. Diffuse pulmonary illness might end in poor lung operate with larger threat for infections and decreased exercise tolerance. These sufferers must be adopted with pulmonary operate testing together with the diffusing capability of carbon monoxide and ratio of residual quantity to total lung capacity. Pathogenesis are (in order of decreasing frequency) dyspnea or tachypnea, polydipsia and polyuria, bone ache, lymphadenopathy, weight loss, fever, gingival hypertrophy, ataxia, and reminiscence issues.

Order generic cytotec line
Small monoclonal proteins that migrate in the - or -globulin fraction are tougher to determine on electrophoresis. Immunofixation electrophoresis is used to confirm a monoclonal protein found on gel electrophoresis. Immunofixation electrophoresis may detect a monoclonal protein not evident on serum protein gel electrophoresis, often as a end result of the protein is in too low a focus or is embedded in the normal polyclonal - or -globulin peak. A presumptive prognosis of essential monoclonal gammopathy can be made with reexamination at approximately 6 months and at applicable intervals, thereafter. Occasional patients may have extreme renal illness related to monoclonal gammopathy. A few p.c of individuals may have biclonal or triclonal gammopathy (see Table 106�1). The prognosis reflects the sum of (1) the monoclonal protein degree, (2) the marrow plasma cell focus (<10 percent), (3) the absence of other features of progressive plasma cell neoplasm. A creating consensus favors measurement of serum protein gel electrophoresis and serum free light chain levels (and the: ratio), and serum protein immunofixation electrophoresis without urinary Ig measurements to detect monoclonal gammopathies. The principal method to remedy is to try and suppress the small B-cell clone and, thereby, its monoclonal protein secretion with chemotherapy. Thus, within the face of significant renal impairment a careful analysis, together with positron emission tomography, should be thought of to exclude a solitary lesion. In distinctive cases, ablative therapy with an autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant could additionally be thought-about. Remarkably, despite very excessive serum copper ranges in the latter instances, no different organ harm ensued. Iritis, vitritus, and maculopathy with loss of visible acuity have also been described in affiliation with a monoclonal gammopathy. IgM monoclonal gammopathy has a considerably larger frequency of neuropathy than does IgG or IgA monoclonal gammopathy. A suggestion has been made to start therapy with intravenous Ig, especially in essential monoclonal IgM-associated neuropathy, because of the relative security of this method. Non�B-cell malignancies, including stable tumors,3,5,6,18,178�181 myeloproliferative issues,182�189 and Hodgkin and T-cell lymphomas,190�193 are related to monoclonal Ig. These relationships may outcome from varied components: (1) patients with a monoclonal Ig have an elevated danger of creating most cancers; (2) the monoclonal Ig is an antibody in opposition to some antigen related to the cancer; (3) the monoclonal Ig is the product of cancer cells; or (4) coincidence. The last chance is favored by two epidemiologic studies that discovered the same frequency of monoclonal gammopathy in a matched management group as in cancer sufferers. Disorders Reported in Coincidence with Monoclonal Gammopathy Axial bone fracture138,139 Connective tissue illnesses and autoimmune illnesses: Crohn disease, cryoglobulinemia, Hashimoto thyroiditis, lupus erythematosus, myasthenia gravis, pernicious anemia, polymyalgia rheumatica, psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, Sj�gren disease140�149 Corneal and different ocular ailments: pseudo�Kayser-Fleischer ring,243 corneal gammopathy102-106,244 Cutaneous ailments: Schnitzler syndrome, urticaria, hyperkeratotic spicules, pyoderma gangrenosum (neutrophilic dermatoses), psoriasis, scleromyxedema150�156 Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis157 Endocrine ailments: hyperparathyroidism158,159 Gaucher disease, kind I160�162 Hepatic illness: cirrhosis,148 hepatitis,163,164 Hereditary spherocytosis165 Infectious diseases: bacterial endocarditis, Corynebacterium species, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, human immunodeficiency virus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, purpura fulminans19,148,166�169,212,215 Metabolic disease: hyperlipidemia170 Neutropenia, chronic85,86,171 Osteoporosis172,174,a hundred seventy five Pituitary macroadenoma173 Pregnancy174 Systemic capillary leak syndrome 177 Carcinomas: colon, lung, prostate, other3,5,6,178�181 Myeloproliferative illnesses: acute and persistent myelogenous leukemia,182�184 persistent neutrophilic leukemia, polycythemia vera185�189 T-cell lymphomas, Hodgkin lymphoma190�193 After chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or marrow, kidney, or liver transplantation194�198,213�215 Miscellaneous diseases200�202 Transient, monoclonal, or oligoclonal gammopathies204�206 Factitious hyperferremia207 Factitious enhance in C-reactive protein208 Vitamin B12 deficiency140,209 relationship in most sufferers. A high frequency of B-cell clonality and IgH gene rearrangements have additionally been described. Following marrow transplantation, the presence of oligoclonal blood B-lymphocyte populations usually reflects the method of reconstitution of the B-cell population. In monoclonal gammopathy of the IgG type, the concentration of monoclonal Ig usually is less than three g/dL. Occasional sufferers with important monoclonal gammopathy have concentrations as excessive as 6 g/dL. Some patients have urinary monoclonal mild chain excretion (Bence Jones proteinuria) as the only real manifestation of monoclonal gammopathy. For instance, sufferers with IgG myeloma normally have very low IgA and IgM concentrations and a reduced polyclonal IgG degree. Chemotherapy, radiotherapy, organ or marrow transplantation,194�199 and different miscellaneous disorders5,7,10,24�26,147,148,200�202 are related to a transient or persistent monoclonal Ig (see Table 106�3). The excessive prevalence of monoclonal proteins and associated ailments, especially after age 50 years, indicates some of these associations are coincidental. Thus, though surgical correction of hyperparathyroidism is related to disappearance of the plasma monoclonal protein,158 statistical research of this dysfunction recommend a coincidental Oligoclonal or monoclonal serum Ig levels have been detected with high-resolution agarose gel electrophoresis in hospitalized patients with acute-phase reactions or polyclonal hyperglobulinemia. Clonally restricted, idiotype-positive blood B cells are characteristic of myeloma however not of monoclonal gammopathy. Its focus in serum regularly is elevated in myeloma, and the magnitude of the elevation is positively correlated with tumor mass. More than 40 variables have been studied as an index for discriminating a secure (benign) from progressive (malignant) clone Table 106�4). No single take a look at is sufficiently sensitive and specific to be helpful in a person affected person.