Lyrica dosages: 150 mg, 75 mg
Lyrica packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 240 pills

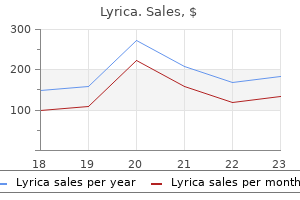
Purchase cheap lyrica online
The hypersecretory response may be exaggerated with intrauterine pregnancy, ectopic being pregnant or trophoblastic disease. Enlarged nuclei are polyploid somewhat than aneuploid, a situation typically seen in adenocarcinoma. Congenital absence of the uterus (agenesis) reflects failure of m�llerian ducts to develop. A section of endometrium shows enlarged, bulbous nuclei that protrude into the gland lumen. Uterus didelphys is a double uterus, as a end result of failure of the 2 m�llerian ducts to fuse in early embryonic life. Uterus duplex bicornis is a uterus with a common fused wall between two distinct endometrial cavities. The frequent wall between the apposed m�llerian ducts fails to degenerate to kind a single uterine cavity. Uterus septus is a single uterus with a partial septum, as a result of incomplete resorption of the wall of the fused m�llerian ducts. Didelphic and bicornuate uterine fusion defects improve the risk of untimely start only barely. Long-standing pyometra may rarely be associated with development of endometrial squamous cell most cancers. Additional problems embrace amenorrhea or, in the event of a subsequent pregnancy, increased abortion charges, preterm labor and placenta accreta. It should be distinguished from the conventional presence of neutrophils throughout menstruation and mild lymphocytic infiltrates at other instances. In most cases of endometritis, findings are nonspecific and barely point to a particular trigger. Curettage is diagnostic and often curative, as a outcome of it removes necrotic tissue that has served as the nidus of the continuing an infection. Nowadays, the condition is of little significance, though it was quite harmful earlier than antibiotics. Pain, dysmenorrhea or menorrhagia correlate with adenomyosis if the glands are 1 mm or more beneath the endometrial myometrial junction, with more extreme signs as glands penetrate more deeply into the myometrium. Microscopic examination exhibits glands lined by proliferative to inactive endometrium and surrounded by endometrial stroma with varying degrees of fibrosis. Secretory modifications are rare, besides during pregnancy or in patients treated with progestins. Extension of hyperplastic or neoplastic endometrium from the endometrial functionalis into adenomyotic foci could occur. These symptoms seem in parous ladies of reproductive age and regress after menopause. The reduce floor of the uterus reveals small, purple areas corresponding to endometrial glands within the myometrium. Pseudodecidual change thus seems early and overshadows the weak glandular growth. Newer contraceptive combinations contain decrease doses of hormones and elicit much less change. Women who use contraceptives containing progestational agents have considerably lower charges of endometrial and ovarian cancer, reflecting the growth-inhibiting properties of progesterone and fewer ovulations (see below). Most instances are associated to a disturbance of the hypothalamic�pituitary�ovarian axis (Table 24-4). As a result, the endometrium remains in a proliferative state dominated by a disordered, cystic glandular appearance and extreme bulk. Thrombosis causes local tissue breakdown resembling that of menstrual endometrium, which the affected person experiences as symptomatic bleeding out of synchrony with different areas of the endometrium. Elevated estrogen levels normally decline, both via delayed ovulation or involution of the stimulatory follicle. If the decline is speedy, the endometrium undergoes a heavy synchronized menstrual circulate.
Cheap lyrica online amex
The final outcome is determined by tumor stage: sufferers with limited disease at diagnosis do higher in comparison with these with widespread (high-stage) illness. In equatorial Africa and Papua, New Guinea, endemic Burkitt lymphoma is the most common childhood malignancy. Its peak incidence is in 4- to 7-year-olds, and it generally entails the jaw, different facial bones and the belly viscera. In endemic instances, the breakpoint on chromosome 14 happens in the heavychain�joining region, as seen in early B cells. Many sufferers experience prodromal polyclonal B-cell activation caused by bacterial, viral or parasitic infections. Lymph node is effaced by neoplastic lymphocytes with a number of starrysky macrophages (arrows). Bone marrow aspirate smear displaying typical cytologic options of Burkitt lymphoma. Diagnosis requires a mixture of medical and laboratory findings, including radiographic research. Patients with sizable cumbersome tumors generally current with Burkitt leukemia and intensive bone marrow involvement. Tissue sections reveal plentiful mitotic figures, reflecting the extremely excessive proliferative rate on this tumor. Thus, up to 90% of people with early stage illness and 60%�80% of these with high-stage illness may be cured. Tumor lysis syndrome can occur when remedy begins, because of fast tumor cell dying. Men are more affected than women, and the illness is proportionately twice as widespread in blacks as in whites. The vertebral column, ribs, skull, pelvis, femurs, clavicles and scapulae are mostly affected. Plasma cells focally fill the medullary cavity, erode cancellous bone and finally destroy the bony cortex, inflicting pathologic fractures. If the tumors breach the bony cortex, they might spread beyond the medullary cavity into surrounding gentle tissues. Long-term survivors of the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki had a 5-fold greater incidence of multiple myeloma. Antigenic stimulation results in reactive, polyclonal proliferation of B cells, which may render them prone to a later mutagenic event, establishing a single malignant clone. In plasma cell myeloma, the peripheral blood commonly exhibits pink blood cells seemingly stacked on each other, like coins in a roll. Cytoplasmic and nuclear inclusions, representing accumulated or partially degraded immunoglobulin, are often present. High ranges of M-protein trigger purple blood cells to stick collectively finish on finish, like a stack of coins. Marked peripheral blood plasmacytosis establishes a analysis of plasma cell leukemia. Neoplastic plasma cells can present variable cytologic options starting from normal-appearing cells (A) to cells resembling blasts (B). Bone destruction in a quantity of myeloma results from both progressive tumor growth and secretion of osteoclast-activating issue by malignant plasma cells. Calcium released from injured or resorbed bone may precipitate within the kidneys (nephrocalcinosis) and impair renal function. Monoclonal light-chain proteinuria can harm renal tubular epithelium and result in kidney failure. M-proteins can suppress regular antibody responses, and so predispose to infectious issues. Anemia develops in 70% of patients, each as a outcome of the neoplastic plasma cells displace regular bone marrow and since renal damage limits erythropoietin production.
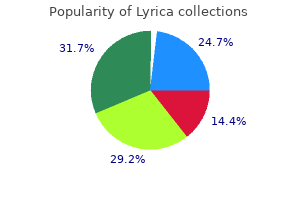
Discount lyrica online visa
Mural thrombi form in atrial or ventricular chambers in 40% of sufferers with rheumatic valvular illness. Rarely, a big thrombus within the left atrial appendage develops a stalk and acts as a ball valve to obstruct the mitral valve orifice. Congestive coronary heart failure complicates rheumatic disease of both mitral and aortic valves. A view of a surgically excised rheumatic mitral valve from the left atrium (A) and left ventricle (B) shows inflexible, thickened and fused leaflets with a slim orifice, creating the attribute "fish mouth" look of rheumatic mitral stenosis. Note that the tips of the papillary muscle tissue (shown in B) are instantly connected to the underside of the valve leaflets, reflecting marked shortening and fusion of the chordae tendineae. The coronary heart of a patient who died of complications of systemic lupus erythematosus displays verrucous vegetations (arrows) on the leaflets of the mitral valve. Adhesive pericarditis often follows the fibrinous pericarditis of acute attacks, however not often causes constrictive pericarditis. Focal inflammatory lesions occur in all layers of the aortic wall, particularly close to the valve ring. Fibrinoid necrosis of small vessels and focal degeneration of interstitial tissue are seen. Verrucous vegetations, as a lot as four mm, happen on endocardial surfaces and are referred to as Libman-Sacks endocarditis. Scleroderma (Progressive Systemic Sclerosis) Cardiac involvement is second solely to renal disease as a reason for death in scleroderma. The myocardium shows intimal sclerosis of small arteries, which leads to small infarcts and patchy fibrosis. Cor pulmonale (due to pulmonary interstitial fibrosis) and hypertensive heart disease (caused by renal involvement) are also seen. Necrotizing lesions in branches of the coronary arteries trigger myocardial infarction, arrhythmias or heart block. Bacterial Endocarditis Is Infection of the Cardiac Valves Fungi, chlamydia and rickettsiae can also cause infective endocarditis, however accomplish that uncommonly. Before the antibiotic period, bacterial endocarditis was untreatable and virtually invariably fatal. The an infection was categorised based on its scientific course as acute or subacute endocarditis. Acute bacterial endocarditis was an infection of normal cardiac valves by extremely virulent suppurative organisms, sometimes Staphylococcus aureus and S. Affected valves have been rapidly destroyed, and patients often died inside 6 weeks from acute heart failure or overwhelming sepsis. Subacute bacterial endocarditis was less fulminant, with much less virulent organisms. Characteristic rheumatoid granulomatous inflammation, with fibrinoid necrosis and palisaded lymphocytes and macrophages, might occur within the pericardium, myocardium or valves. Ankylosing Spondylitis A characteristic aortic valve lesion develops in as much as 10% of sufferers with long-standing ankylosing spondylitis. Intravenous drug abusers inject pathogenic organisms together with illicit medicine, and bacterial endocarditis is a infamous complication. The commonest supply of micro organism in intravenous drug abusers is the skin, with S. Prosthetic valves are sites of an infection in 15% of instances of endocarditis in adults, and 4% of sufferers with prosthetic valves have this complication. Most of the remainder are caused by gram-negative cardio organisms, streptococci, enterococci and fungi. Examples embrace dental procedures, urinary catheterization, gastrointestinal endoscopy and obstetric procedures. Antibiotic prophylaxis is beneficial during such maneuvers for sufferers at elevated risk for bacterial endocarditis. Degenerative adjustments in heart valves, including calcific aortic stenosis and calcification of mitral annuli, predispose to endocarditis. Infection of previously broken valves by less virulent organisms has been tied to (1) hemodynamic factors, (2) formation of an initially sterile platelet�fibrin thrombus and (3) adherence properties of the microorganisms. Lesions kind on the influx portions of valves, where high pulsatile shear stresses happen. The pressure gradient across a slim orifice (valve or congenital defect) produces turbulent circulate on the periphery and a high-velocity jet at the middle, both of which are inclined to denude valve endothelial surfaces.
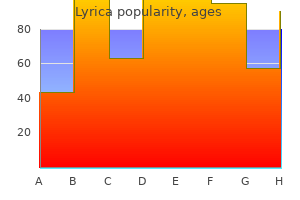
Order lyrica 150 mg with visa
The vascular tree is a circuit that conducts blood from the center by way of large-diameter, low-resistance conducting vessels to small arteries and arterioles, which decrease blood strain and protect the capillaries. The capillaries are thin walled and allow the trade of nutrients and waste merchandise between tissue and blood, a process that requires a really massive surface area. The circuit back to the heart is accomplished by the veins, that are distensible and provide a quantity buffer that acts as a capacitance for the vascular circuit. Many veins, particularly in the extremities, have valves made from endothelial-lined folds of the tunica intima, which stop backflow and assist to transfer blood under the low stress of the venous circulation. Postcapillary venules are the site of leukocyte transmigration into tissue in inflammatory reactions (see Chapter 2). Fenestrae interrupt the continuity of the inner elastic lamina, allowing smooth muscle cells to migrate from the media into the intima. The intima of muscular arteries, like that of the aorta, additionally incorporates small numbers of easy muscle cells, connective tissue and occasional inflammatory cells. Vasa vasorum are present within the outer wall of thicker muscular arteries, but not in smaller ones. As the vascular tree branches further, the tunica media becomes thinner, and except for the endothelium, the tunica intima disappears. Their slender lumens improve resistance, thereby lowering blood stress to ranges appropriate for trade of water and plasma constituents throughout downstream thinwalled capillaries. The small muscular arteries, also known as resistance vessels, assist to preserve systemic strain by regulating complete peripheral resistance. Lymphatics Drain Interstitial Fluid Lymphatic circulation consists of blind-ended lymphatic capillaries, consisting of (1) endothelium with no pericytes; (2) precollecting lymphatics; and (3) amassing lymphatics, which pump lymph towards the lymph nodes, lymphatic trunks and at last thoracic and proper lymphatic ducts, which return lymph back to the blood. Filtrate from capillaries and venules enters the lymphatics, which act as a pathway to regional lymph nodes for cells, foreign material and microorganisms. The collecting lymphatics have an intrinsically contractile layer of easy muscle cells that propel lymph ahead. They have an endothelial lining surrounded by one or two layers of smooth muscle cells. Capillaries Permit Transport from the Blood to the Interstitium In these smallest blood vessels, particularly, capillaries, the endothelium is supported solely by sparse smooth muscle cells. The capillary endothelium offers for exchange of solutes and cells between blood and extracellular fluid. A needed characteristic of this exchange is a marked lowering of strain, which prevents intravascular fluid from shifting into the extracellular area. The capillary endothelium is a semipermeable membrane, during which change of plasma solutes with extracellular fluid is managed by molecular measurement and cost. Brain capillaries are extremely impermeable as a end result of junctions between endothelial cells are tightly sealed, preventing trade of proteins across the vessel wall. Transport in different capillary beds is mediated either by passage of molecules through incomplete cell junctions or by pinocytosis, a process by which molecules traverse the cytoplasm through vesicular transport. Some investigators have advised that vesicles are related with each other to provide a channel for direct transport of plasma proteins throughout the cytoplasm. In some locations, the capillary endothelium itself may have permanent channels by way of discontinuous gaps between them. Fenestrated capillaries in renal glomeruli are specifically adapted to filter plasma. A Single Endothelial Cell Layer Forms a Thromboresistant Barrier Endothelial cells are metabolically energetic and are intimately concerned in a number of biological capabilities, including vascular permeability, coagulation, platelet regulation, fibrinolysis, irritation, immunoregulation and restore. They additionally modulate vascular clean muscle cell operate via paracrine pathways. Endothelial cells kind distinctive mechanotransduction structures that modulate the effects of luminal hemodynamic shear stress on the vessel wall. This impact activates biochemical signaling and leads to expression of vasoactive compounds, growth components, coagulation/fibrinolytic/ complement factors, matrix degradation enzymes, inflammatory mediators and adhesion molecules.
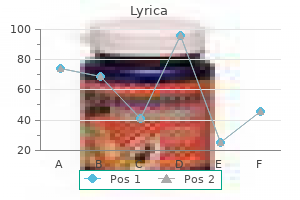
Generic lyrica 75 mg on-line
In experimental cardiac hypertrophy, "fast" -myosin is replaced by "gradual" -myosin, resulting in impaired myocardial contractility. However, this modification in myosin gene expression can also be adaptive, because it increases the strain generated throughout systole and improves contraction effectivity, thus conserving power. Hypertrophied hearts exhibit similar, but not similar, adjustments in myosin isoforms. Ventricles include only sluggish myosin, and hypertrophic hearts change from fast to gradual myosin solely within the atrium. Current research focuses on methods to exploit this capability so as to exchange damaged or necrotic muscle. After delivery, however, the center downregulates glycolytic enzymes and increases expression of genes that encode proteins mediating -oxidation of fatty acids derived from breast milk. The failing coronary heart reverts to using glucose by reexpressing fetal patterns of genes for power technology. Recent advances in understanding the molecular pathogenesis of coronary heart failure have identified a task for histone acetylases and deacetylases in stress-activated myocyte signaling pathways. This change entails changes in subcellular localization and activities of histone acetylases and deacetylases, suggesting that manipulation of histone-modifying enzymes may be helpful in stopping heart failure. Apoptosis of cardiac myocytes will increase 5-fold in animal models of heart illness, and senescent rats have 30% fewer cardiac myocytes than do younger ones. Pathologic hypertrophy is generally associated with larger cardiac myocyte apoptosis, which may help transition from compensated hypertrophy to heart failure. Thus, various signaling pathways in cardiac hypertrophy may exert each proapoptotic and antiapoptotic influences, the final end result relying on the stability between them. These increase in quantity with age or in illness, indicating a capability for nuclear division. Ischemic coronary heart illness is by far the most typical reason for cardiac failure, accounting for greater than 80% of deaths from heart disease. Most of the remaining are brought on by nonischemic heart muscle illness (cardiomyopathies) and congenital heart ailments. Ventricular hypertrophy is seen in nearly all circumstances associated with continual coronary heart failure. Initially, only the left ventricle could additionally be hypertrophied, as in compensated hypertensive heart illness. But when the left ventricle fails, some proper ventricular hypertrophy often follows, because the elevated workload is imposed on the proper ventricle by the failing left ventricle. In most instances of clinically apparent systolic heart failure, the ventricles are conspicuously dilated. The distribution of endorgan involvement is decided by whether or not the center failure is predominantly left sided or right sided. Left-sided heart failure is more widespread, as the most common causes of cardiac harm. To compensate for left ventricular failure, left atrial and pulmonary venous pressures rise, resulting in passive pulmonary congestion. Alveolar septal capillaries fill with blood and small ruptures enable erythrocytes to escape. As a result, alveoli contain many hemosiderin-laden macrophages (so-called coronary heart failure cells). If capillary hydrostatic stress exceeds plasma osmotic stress, fluid leaks from capillaries into alveoli. Resultant pulmonary edema (see Chapters sixteen and 18) could also be large, with alveoli being "drowned" in a transudate. Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis outcomes when congestion is present over an prolonged period. Right-sided heart failure most commonly complicates left-sided failure, however it can develop independently because of intrinsic lung illness or pulmonary hypertension. The latter creates resistance to blood circulate via the lung, inflicting proper atrial strain and systemic venous strain to improve.
Order genuine lyrica on line
Growth patterns could additionally be cribriform, micropapillary, papillary, stable and comedo varieties, and a number of architectural patterns can coexist in one lesion. The cells have plentiful cytoplasm, irregular nuclei with distinguished nucleoli and coarse chromatin. The mobile necrotic debris typically undergoes dystrophic calcification, which can be seen on mammography as linear, branching calcifications. Intraductal carcinoma with a cribriform architecture and central comedo necrosis (arrows). Intermediate-grade ductal carcinoma in situ with moderate nuclear pleomorphism and some polarization of cells around secondary spaces. A small proportion of girls current symptomatically with a mass lesion, a nipple discharge or Paget illness of the nipple (see below). Breast-conserving surgical procedure is possible in lots of cases, and adjuvant radiation reduces the chance of recurrence. When tumors recur, they achieve this at the site of the previous surgery and are invasive carcinomas 50% of the time. Stains for myoepithelial cell markers (smooth muscle myosin heavy chain, calponin, p63, etc. They are well-circumscribed, partially cystic, incessantly hemorrhagic, stable lots. At its edge, the tumor has a easy pushing border, although frank stromal invasion may be present; that is sometimes invasive carcinoma of no particular kind. Fibrovascular cores lined by malignant epithelial cells, without an intervening myoepithelial cell layer. The dermis contains clusters of ductal-type carcinoma cells that are bigger and have extra abundant pale cytoplasm (arrows) than surrounding keratinocytes. Paget cells genetically resemble underlying tumor cells in the vast majority of cases. Prognosis is a operate of the stage of the underlying breast cancer and not the presence of Paget cells. Some proof supports a precursor function for these lesions, albeit not an obligate one: a disproportionately excessive number of tumors that develop are invasive lobular carcinoma, and 2/3 occur in the ipsilateral breast. This protein performs an important role in cell adhesion and in cell cycle regulation by way of the -catenin/Wnt pathway. Patients with germline mutations in this gene are at a excessive risk of creating lobular breast carcinoma and gastric signet ring cell carcinoma. The lumina of the terminal duct lobular items are distended by tumor cells, which exhibit round nuclei and small nucleoli. Lobular carcinoma in situ displaying classic nuclear features however central expansile comedo necrosis. A dyshesive inhabitants of markedly atypical epithelial cells with central comedo necrosis fill and distend the ducts. Dissociation of the neoplastic cells gives rise to areas which may be misinterpreted as secondary areas. Membranous E-cadherin expression is seen in residual luminal epithelial cells, but the lobular neoplastic cells should show loss of staining. However, adjuvant hormonal therapy may be thought of, and lifelong follow-up is required. Invasive Ductal Carcinoma, No Special Type Of invasive breast cancers, 50%�70% fall in this category. Patients most often have an ill-defined breast mass, which can be adherent to the skin or underlying muscle. These largely appear radiologically as a spiculated mass or architectural distortion, with or without associated microcalcifications. An irregularly shaped, dense mass (arrows) is seen in this in any other case fatty breast. Photomicrograph exhibiting irregular cords and nests of invasive ductal carcinoma cells invading stroma. In distinction to invasive ductal carcinoma, the cells of lobular carcinoma tend to type single strands that invade between collagen fibers in a diffuse pattern. If a special-type element makes up over 50% of the tumor, the tumor is considered mixed.
Buy 75 mg lyrica otc
Deficiencies of anticoagulants, corresponding to protein C and antithrombin, improve the incidence of venous thromboembolism. Lymphatic Obstruction Causes Lymphedema Lymphatics may be obstructed by scar tissue, intraluminal tumor cells, pressure from surrounding tumor tissue or plugging with parasites. As collateral lymphatic routes are plentiful, lymphedema (distention of tissue by lymph) normally occurs solely when main trunks are obstructed, especially in the axilla or groin. For example, when radical mastectomy for breast cancer was routine, axillary lymph node dissection frequently disrupted lymphatic channels and led to lymphedema of the arm. Prolonged lymphatic obstruction causes progressive dilation of lymphatic vessels, or lymphangiectasia, and overgrowth of fibrous tissue. In the tropics, filariasis, by which a parasitic worm invades lymphatics, is a standard explanation for elephantiasis (see Chapter 9). It often impacts just one limb, but it may be more in depth and contain the eyelids and lips. They are important for normal tissue fluid stability, providing drainage of plasma filtrates, cells and international materials from the interstitial spaces. They are also important in fats digestion, by way of lacteals in the intestinal villi, and in immune surveillance. Lymphatic vessels are extra permeable than blood vessels, in part as a end result of the former have fewer tight junctions. This lesion is more correctly considered lymphangiectasia quite than merely lymphedema. Hemangiomas Are Common Benign Tumors of Vascular Channels Hemangiomas normally occur within the skin but may also be found in inside organs. The most typical sites are skin; subcutaneous tissues; mucous membranes of the lips and mouth; and internal viscera, including spleen, kidneys and liver. Capillary hemangiomas range from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. They grow quickly within the first months of life, start to fade at 1�3 years of age and fully regress in most (80%) cases by 5 years of age. Occasionally, the vascular channels rupture, causing scarring and accumulation of hemosiderin. They also seem on mucosal surfaces and visceral organs, together with the spleen, liver and pancreas. If they occur within the mind, they may enlarge slowly and trigger neurologic signs after long quiescent periods. A cavernous hemangioma is a red-blue, delicate, spongy mass, with a diameter of up to a quantity of centimeters. Large endothelial-lined, blood-containing spaces are separated by sparse connective tissue. Cavernous hemangiomas can undergo a selection of adjustments, including thrombosis, fibrosis, cystic cavitation and intracystic hemorrhage. Two or extra tissues could additionally be involved, similar to pores and skin and nervous system or spleen and liver. Other carefully associated lesions are plexiform or racemose angiomas, cirsoid aneurysms and angiomatous dilation of vessels of the mind and elsewhere. Spindle cell hemangioendothelioma happens principally in males of any age, usually within the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of distal extremities. It options vascular, endotheliallined spaces into which papillary projections extend. The evidence favoring hamartoma consists of (1) the lesion is current at delivery; (2) it grows only as the the rest of the physique grows and stays restricted in dimension; and (3) after progress ceases, it usually stays unchanged indefinitely absent trauma, thrombosis or hemorrhage. The development of these vascular malformations remembers the embryology of the vascular system. A network of endothelial channels undergoes remodeling, buying a muscular coat and adventitia. In this view, vascular malformations replicate the persistence of the unique or modified channels and mixtures of connective tissue parts derived from the mesenchyme. At current, hemangiomas are classified by histologic kind and site, though molecular characterization will doubtless lead to new classifications and better understanding of the prognosis of given lesions. Angiosarcoma Is a Rare Malignant Tumor of Endothelial Cells these tumors happen in either intercourse and at any age. Glomus Tumor Is a Painful Tumor of the Glomus Body Glomus bodies are regular neuromyoarterial receptors that are delicate to temperature and regulate arteriolar flow.