Zantac dosages: 300 mg, 150 mg
Zantac packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Discount zantac 150 mg on-line
Mouse adapter to avoid multiple clicks or cursor tremor Utensils with accelerometers and pivot motors that may cancel tremor frequency Surgical treatment Surgical intervention is an possibility for those people whose tremor stays disabling despite enough trials of optimum pharmacologic remedy. As with any surgical process, care ought to be utilized in selecting a surgeon who has sufficient procedural volume to keep skills in these stereotactic surgical strategies. Untreated important tremor could be very disabling, so pharmacologic and, if wanted, surgical intervention have very favorable outcomes which will justify risks of treatment. Druginduced tremor Some degree of tremor happens in all human beings and is usually referred to as physiologic tremor. In scientific follow, the term enhanced physiologic tremor is regularly used to check with tremor exacerbated by medication or circumstances that improve adrenergic exercise. Differentiating druginduced tremor from other causes of tremor requires a thorough history and bodily examination of the patient. A temporal relationship to the initiation of pharmacologic therapy could be very useful in making the diagnosis. Tremor severity is usually dose dependent and improves with cessation of the drug. Druginduced tremor is usually symmetric in nature, predominantly happens throughout posture and action, and is of low amplitude and excessive frequency (10�12 Hz). The exception is druginduced parkinsonian tremor that happens at relaxation and could be uneven in onset. A list of gear and medications which are related to tremor is offered in Table three. Because valproate is usually prescribed for numerous neurologic issues, together with epilepsy, migraine prophylaxis, and mood stabilization, tremor as a end result of this drug is also common. Alcohol withdrawal classically has an related postural tremor, and alcoholism may cause tremor as a downstream effect of chronic liver disease. This is as a end result of most sufferers with druginduced tremor have lowamplitude postural tremor. Other necessary fiber tracts in tremor manufacturing embody thalamocortical loops and tracts from the brainstem to the basal ganglia. It is most likely going that these loops arrange oscillations in motor management at various frequencies, and theoretically these oscillations reverberate to create tremor. It is important to notice that dopamine blocking brokers additionally include antiemetic medication similar to metoclopramide. Parkinsonian tremor Classic parkinsonian tremor is uneven in onset, occurs at relaxation, and turns into less outstanding with posture and action. It has been described as a "tablet rolling" tremor as it sometimes affects the thumb and index finger, mimicking the motion of rolling a capsule between these two digits. Although normally relaxation tremor is predominant, tremor could additionally be present with posture, and motion; on this case, the clinician pays more attention to which tremor state has a greater degree of tremor than others. Clinically, this distinction could be difficult at times as, when a tremor turns into more severe, it could move from a extra pure rest tremor to be current with posture and intention. One key scientific point right here is that the tremor will typically be more extreme with one of these positions. In 2011, the United States Food and Drug Administration approved the use of DaTscans to detect dopamine transporters (DaT) in people with parkinsonian syndromes. An instance of this would be a affected person on valproate or lithium for mood stabilization purposes, who could be switched to lamotrigine, which is much less prone to trigger tremor but continues to be an effective agent. If none of these are choices, then use of a tremorreducing agent corresponding to propranolol or a benzodiazepine is a consideration. Although nearly all of parkinsonian tremor instances will reply to dopaminergic drugs, not all sufferers will respond; some parkinsonian tremors could be very immune to remedy. In these instances, one possibility is to use an anticholinergic treatment such as trihexyphendyl or benztropine. These should be used rigorously in aged sufferers due to the potential unwanted effects of anticholinergic medicines. Also included in this category are antiemetics like metoclopramide, promethazine, prochlorperazine. The diagnosis of practical tremor may be difficult, and infrequently would require referral to a motion disorders specialist. Diagnosis relies on exclusion of natural causes of tremor and supported by acute onset and resistance to therapy.
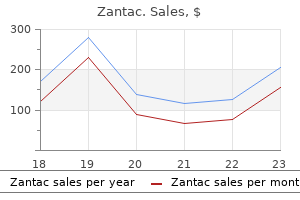
Order zantac american express
Conversely, rarefaction at the oval window leads to compression on the spherical window (dim brown arcs). Pressure waves of different frequencies cross by way of the cochlear duct at different locations along the base-to-apex axis. The highest frequency sounds, about 20 kHz, displace the cochlear duct at the base, and the bottom frequency ones, about 5�10 Hz, at the apex. Note that the bony cochlea is broad at its base and slim on the apex but that the orientation of the cochlear duct is reversed, narrow at the base and extensive at the apex. Between the scala vestibuli and scala tympani runs the cochlear duct, the sensory area of the cochlea. The cochlear duct separates the scala vestibuli and scala tympani for most of their lengths, ending just wanting the cochlear apex, where the helicotrema joins the 2 canals. The cochlear duct shares one wall with the scala vestibuli and one wall with the scala tympani. Like the scala vestibuli and scala tympani, the cochlear duct is full of fluid however the fluid in the cochlear duct is endolymph somewhat than perilymph (see more later). Importantly, the cochlear duct is flexible, in order that stress waves transfer the cochlear duct up and down. Because the cochlea is surrounded by unyielding bone, two pressure valves are wanted to support any movement of the fluid inside. Compression on the oval window results in rarefaction at the spherical window, and rarefaction on the oval window produces compression of the spherical window. Airborne sounds that arrive at different frequencies arrange actions of the oval window at corresponding frequencies. The motion of the oval window in flip sets up a pressure wave at a given frequency that travels by way of the cochlea. Thus, pressure waves at the highest frequency represented in the human cochlea (20,000 Hz) move the cochlear duct at the base of the spiral; pressure waves with low frequencies (less than 200 Hz) move the cochlear duct closest to the helicotrema. An important mechanism of tonotopy is the pliability of the stiffest a part of the cochlear duct, the basilar membrane. Recall that the basilar membrane forms the border between the cochlear duct and the scala tympani. Note that the size of the bony cochlea and those of the cochlear duct are inversely organized: � the narrowest a part of the cochlear duct is positioned at the widest part of the bony cochlea. The slender basilar membrane at the base of the cochlea is stiffest and therefore moves maximally in response to high-frequency pressure waves. In distinction, on the apex of the cochlea, the extensive basilar membrane is comparatively loose and bends maximally in response to low-frequency strain waves. Consequently, the basilar membrane moves maximally in response to sounds of progressively decrease frequencies as one strikes from the base of the cochlea to its apex. This topographic association of maximal strain wave tour alongside the length of the cochlea follows a tonotopic group. The tonotopy of the basilar membrane dictates a tonotopic neural response to sound so that the apical cochlea responds best to low-frequency sounds and the basal cochlea responds greatest to sounds of excessive frequency. The frequency that produces the greatest movement of the basilar membrane, and consequently the best hair cell response at anyone point within the cochlea, is termed the attribute frequency. Dividing the organ of Corti from the relaxation of the cochlear duct is the tectorial membrane, which emanates outward from the modiolus, the central pillar of the cochlear spiral. Sensory hair cells sit atop the basilar membrane and prolong mobile extensions termed stereocilia into the scala media, the fluid chamber of the organ of Corti. At the outer fringe of the cochlear duct is a specialised tissue, the stria vascularis, which pumps potassium ions into the scala media to type endolymph. Endolymph is a potassium ion-rich fluid that fills the scala media, the fluid-filled portion of the cochlear duct. The organ of Corti incorporates two kinds of hair cells, inside and outer, and the tectorial membrane (tm). Spiral ganglion cells (blue) innervate a single row of inner hair cells (blue) and carry afferent input from the inside ear to the cochlear nuclei within the hindbrain. Efferents arising from cells in the pons (maroon) innervate three rows of outer hair cells (maroon). B: the stereocilia of outer hair cells (ohc) are embedded in the tectorial membrane.
Syndromes
- Eat foods that are naturally low in fat such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Have everyone wash their hands before eating.
- Nephrocalcinosis
- Poor visual tracking or blindness
- Other blood tests to look at muscle enzymes (creatine kinase) and possibly a test for Lyme disease or a connective tissue disorder
- Poor judgment
Cheap zantac 150mg with visa
Consequently, lesions of these nerves result in problems with speech, swallowing, and choking or aspiration. This nerve offers motor innervation to two muscular tissues: the trapezius, involved in shrugging, and the sternocleidomastoid. Contraction of the sternocleidomastoid muscle rotates the pinnacle to the contralateral side. Iatrogenic harm of the spinal accent nerve can occur during medical procedures on the neck such as cervical lymph node biopsies. One sign of damage to the innervation of the trapezius muscles is a winged scapula in which the shoulder blade juts out from the rib cage, a condition that limits the ability to carry out on a daily basis actions. The hypoglossal nerve innervates the muscular tissues of the tongue, that are critical to respiratory, consuming, swallowing, speech, emesis, and a myriad of other capabilities similar to communicating anger through a particularly immature gesture. Testing reveals that the affected person sees normally out of every eye when the opposite eye is covered. Now you know that the issue is with gaze management rather than with visual processing. Of the three cranial nerves that would give rise to misalignment of the eyes, oculomotor is the most probably culprit as a outcome of it innervates four muscle tissue in comparison with the one apiece innervated by the abducens and trochlear nerves. Such a finding provides impetus to test the remaining capabilities of the oculomotor nerve: eyelid elevation whereas looking up, the pupillary light reflex, and near vision, all or any of which can be affected. An particular person with a lesioned facial nerve is unable to make a facial features on the affected side underneath any circumstance. An abducens nerve lesion would prevent any motion, for any reason, of the eye to the facet. In distinction, a central lesion might impair lateral gaze shifts but not reflexive lateral eye actions; it is a common drawback amongst people with a number of sclerosis, a central demyelinating disease (much more on this in Chapter 19). Conglomerations of symptoms that could not arise from injury of a single site in the brain are sometimes because of a disease course of. Some illnesses produce anatomical lesions of neural parts that share a selected molecular vulnerability. An example of that is a number of sclerosis in which a myelin-related molecule fails to function properly. For instance, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis leads to the demise of neurons inside choose pathways supporting voluntary movement. For instance, weakness in all skeletal muscular tissues of each eyes, extraocular and levator palpebrae superioris alike, might only outcome if the oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens nerves on each side had been damaged. However, no parasympathetic symptoms are observed in continual progressive external ophthalmoplegia, a mitochondrial muscle disorder that, over time, produces a paralysis of all skeletal muscular tissues across the eye without any autonomic signs. This unlucky illness eventually affects the lengthy muscles of the limbs and torso, inflicting the affected person great issue in standing and walking, as properly as in eye movements. Oral and pharyngeal reflexes in the mammalian nervous system: Their various range in complexity and the pivotal position of the tongue. However, most of the modern world now views folks with out mind perform as dead as well. The swap from unique cardiac demise to cardiac-or-brain-death took place in the second half of the 20th century as a response to two medical developments. First, the development of respirators and different palliative technology allowed patients with out mind perform to continue to beat their hearts. Thus was born the idea that folks with a beating coronary heart however no brain perform are useless. The legal necessities for brain demise within the United States are that a patient should stop breathing, termed apnea; show no intact brainstem reflexes, such because the corneal and pupillary gentle reflexes; and not react to painful stimuli. The last authorized requirement is peculiar from a strictly neurobiological perspective because the spinal wire helps reactions to noxious stimulation of the hands, toes, and different elements of the physique. The persistent vegetative state stands in a markedly completely different legal class from brain demise. In persistent vegetative state, an intact brainstem supports physiological life, however a lack of any forebrain function signifies that that life is without which means. The conduct of individuals in a persistent vegetative state stems entirely from the brainstem and spinal wire. Essentially, the persistent vegetative state isolates and brings to the fore the capabilities of the brainstem.
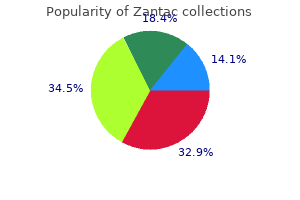
Order zantac us
Rivastigmine, donepezil, zopiclone, and pramipexole have also been reported to be effective in several small openlabel studies. Increased muscle exercise throughout speedy eye movement sleep corre lates with lower of striatal presynaptic dopa mine transporters. Restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movements throughout sleep: analysis and therapy. Prevalence of stressed legs syndrome and periodic limb motion dysfunction in the common population. All the mistaken moves: a medical evaluation of stressed legs syndrome, periodic limb actions of sleep and wake, and periodic limb movement disorder. Foot tapping, nail biting, arm waving, hand flapping, and different repetitive actions and behaviors may be seen frequently with spectators at a baseball recreation culminating to its peak, while the participant at bat could interact in his personal sequence of idiosyncratic repetitive actions prior to taking his position over the plate. Young kids are more probably to display ritualistic and repetitive behaviors and movements that appear to be part of their regular repertoire. As stereotypies are related to developmental abnormalities together with autism and psychological retardation, a neurological foundation for the phenomenon is suspected, with some investigators suggesting dysfunction of cortico�striatal�thalamo�cortical circuitry. As stereotypies are noted with socially isolated animals, some emphasize social isolation as a key to look of continual stereotypic conduct, thus viewing autism and mental retardation as a form of sensory deprivation and stereotypies being a means of the person to improve selfstimulation. Familial aggregation of stereotypies may result in genetic studies in the future. Definitions Patterned repetitive movements have been classified as stereotypies, habits, compulsions, and mannerisms, and overlapping definitions are widespread. Whatever the definition, repetitive movements would possibly come to consideration when patterns turn out to be unusually noticeable, are peculiar in look, or trigger interference with daily activities. A commonly used definition of stereotypies is "involuntary or unvoluntary, coordinated, patterned, repetitive, rhythmic, seemingly purposeless actions or utterances. They could occur many occasions day by day and have a tendency to proceed in a rather fastened pattern of frequency and appearance for months and sometimes a few years. Episodes are characterised as paroxysmal events occurring for a couple of seconds; however, prolonged intervals of movement might happen, often with stereotypies occurring at instances of boredom or imaginative exercise. The episodes may be quite much like each other in look, length, and the scenario by which they may appear. A usually developed baby may exhibit one stereotypic movement over extended periods of time. However, the characteristics of the stereotypic motion might change over the years from infancy to early or late childhood. For example, an toddler presenting with distal upper and decrease extremity twirling could progress over time to have a typical bilateral arm motion, or initial excessive amplitude hand flapping might give method over time to a less pronounced finger posturing. On repetitive behaviors occurring a minimum of as soon as daily, 679 parents reported spinning (59. Though not triggered particularly by a single occasion, stereotypies could occur in specific stimulating situations such as whereas a baby is joyous, excited, or in anticipation. Teachers might describe movements in the classroom, typically during episodes of lapsed consideration. The widespread appearance of stereotypic move� ment consists of any mixture of bilateral finger, hand, and/or arm movement or posturing, called advanced motor stereotypies by some experts. This may include wiggling or twirling of the fingers ("piano playing"), excessive amplitude hand or arm flapping, or numerous posturing of the arms, hands, or fingers in a flexion or extension position. The arms may be elevated at the sides of the body creating a "flying" appearance during hand flapping or finger twirling or could also be positioned in a neutral down going position. The arms are typically placed in the midline, posturing and wiggling together, giving the looks of "hand washing. Some instances are accompanied by further physique actions during hand motion corresponding to leaping, crouching, or truncal posturing. Episodes of higher limb movement usually last for several seconds; nevertheless, extended episodes lasting more than a minute are rare. Nodding is a steady toandfro motion that may proceed for prolonged periods of time.
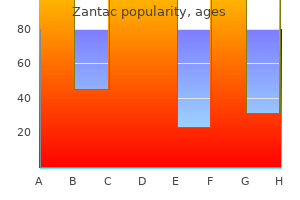
Cheap zantac generic
Because of this early bilateralization of auditory data, the left and right sides of the brain process input from both the left and proper ears. Therefore, the only traumatic accidents that may render an individual deaf are within the cochlea, the vestibulocochlear nerve, or a cochlear nucleus. The center cerebellar peduncle types the bulk of the attachment of the cerebellum to the brainstem in addition to the lateral partitions of the fourth ventricle. The superior cerebellar peduncles, seen in the dorsolateral roof of the fourth ventricle, carry the output of the cerebellum destined for midbrain and forebrain. The most remarkable landmarks of the pons are the premise pontis, the center cerebellar peduncle (mcp), the fourth ventricle, and the overlying cerebellum. Fibers descending from the cerebral cortex include corticospinal fibers, reduce in cross-section (circled x in A) en path to the spinal wire, and corticopontine fibers that terminate in the pontine nuclei. Pontine nuclear neurons ship axons across the midline, reduce longitudinally in this transverse section (arrowhead in A), and into the center cerebellar peduncle to reach their cerebellar targets as mossy fibers. B: the pons is divided into two divisions: the ventral foundation pontis and the dorsal pontine tegmentum. The remaining buildings of interest are positioned in the pontine tegmentum and cerebellar peduncles. The spinothalamic tract (stt) travels lateral to the ventral edge of the medial lemniscus (ml), which is now diagonally oriented. Together, these two tracts carry all kinds of somatosensory data from the contralateral body. After the facial genu, facial motoneuron axons travel ventrolaterally and caudally from the genu to exit laterally on the stage of the pontomedullary junction. The medial longitudinal fasciculi (mlf) stay on either side of the dorsal midline. Photomicrograph reprinted and drawings modified with permission from deArmond S et al. Just because the pyramids define the medulla, the premise pontis denotes pontine territory. As they cross by way of the pons, many corticospinal fibers give off collaterals that contact neurons within the pontine nuclei. Fibers that descend from cortex to reach pontine nuclear neurons both solely or as collaterals comprise a corticopontine tract. Pontine nuclear neurons, in turn, ship axons throughout the midline and through the center cerebellar peduncle into the cerebellum. Within the tegmentum are found the medial lemniscus and spinothalamic tract, each of which have shifted in orientation relative to medullary levels. The medial lemniscus carries tactile, vibratory, and proprioceptive information from the contralateral legs, trunk, and arms. Lateral to the ventrolateral fringe of the medial lemniscus, the spinothalamic tract carries pain and temperature information from the contralateral body toward the ipsilateral thalamus and thence to somatosensory cortex. The cranial nerve nuclei present are a unique group than these current in the medulla. Only one leftover is present: a vestige of the spinal trigeminal nucleus, its rostral pole. During development, the facial motoneurons migrate dorsally toward the ventricle after which ventrally again, all the while dragging their axons behind them. This peculiar process ends in a hairpin pathway for the axons of branchiomeric facial motoneurons. Only facial nerve axons of motoneurons innervating branchial arch�derived muscles-the superficial facial muscular tissues and the stapedius-follow the circuitous route across the abducens nucleus. Somatosensory fibers from the ear, destined for the trigeminal nuclei, and style enter destined for the nucleus of the solitary tract enter the brainstem by way of the nervus intermedius. The abducens nucleus is a compact spherical nucleus containing motoneurons that innervate the lateral rectus muscle, which, as you recall, abducts the eye.
Purchase zantac 150mg visa
While this low stage of spontaneous launch is unlikely to elicit an action potential, it could change the membrane potential or alter excitability. In essence, untriggered, spontaneous vesicle fusion can produce a big background hum within the neuronal conversations of the mind. The molecules, membrane area, and mechanisms of spontaneous release appear to partially, however not fully, overlap with those of triggered synchronous release. Thus, at relaxation, single vesicles of neurotransmitter are released intermittently, maybe in affiliation with stochastic openings of single calcium channels. Then, when an motion potential triggers enough calcium ion influx, fusion pores are fashioned at multiple terminals and neurotransmitter spills concurrently into a number of synaptic clefts. Now, think about the consequences of shedding voltage-gated calcium channels, as occurs in Lambert-Eaton syndrome. More action potentials are required for a triggering focus of calcium ions to enter via fewer voltage-gated calcium channels. Exciting recent findings recommend that spontaneous launch is crucial to formation and stabilization of synapses during improvement. For instance, if spontaneous launch from a presynaptic terminal plummets, perhaps due to harm or disease, a compensatory enhance in synaptic efficacy will outcome. One mechanism by which synaptic efficacy can be increased is by the insertion of extra postsynaptic receptors. Upon sufficient depolarization, some small variety of vesicles fuses with the plasma membrane and dumps neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. The common variety of vesicles launched per action potential varies from tons of at the neuromuscular junction to one at many central synapses. A difference within the number of lively zones per synapse largely explains this variation. Many central synapses, such as these within the hippocampus, include a single energetic zone, whereas the neuromuscular junction accommodates tons of of energetic zones. When a single motion potential arrives at an lively zone, either a vesicle is launched or no vesicle is released. Put into probabilistic phrases, the chance of release can range between zero-release by no means happens-and one-release occurs in response to every action potential. The decrease variety of energetic zones and thus vesicles launched at central synapses allows one postsynaptic cell to receive and sum up info from a number of inputs. A low variety of lively zones per synapse, and thus a low number of vesicles released per action potential, prevents a ceiling impact for each synaptic input. Since one vesicle is released at every lively zone and there are hundreds of energetic zones, hundreds of vesicles are released per motion potential within the presynaptic axon. This arrangement prevents a ground effect, that means that when an motion potential arrives within the motoneuron, the sole source of enter to a muscle fiber, the effect shall be massive enough to be positive that the muscle responds. Thus, an action potential within the motoneuron innervating a skeletal muscle reliably causes a muscle fiber twitch. As it seems, the plasma membrane at the active zone is endocytosed within the terminals of active neurons. The endocytosed membrane accommodates contributions from the fused vesicle along with lipids and proteins native to the plasma membrane. The membrane components are sorted, and useful synaptic vesicle proteins are used to make new synaptic vesicles, whereas synaptic vesicle proteins which may be now not good are transported to the cell physique for degradation. There are two major routes for recycling vesicles: � Enough clathrin-coated membrane to form a person vesicle is endocytosed and types a new vesicle in a matter of seconds. Under these circumstances, clathrin, a protein that self-assembles into basketlike structures, coats simply sufficient plasma membrane on the energetic zone to kind a single vesicle. Recycled vesicles are then refilled with neurotransmitter by way of processes described in Chapter 12. At faster rates of launch, a bigger area of membrane, including membrane from many vesicles, is taken up via bulk endocytosis into endosomal buildings. From these endosomes, a small area of membrane turns into coated with clathrin and then buds off as a single synaptic vesicle. Because of its small dimension, the readily releasable pool might, in concept, be depleted by fewer than two dozen action potentials occurring at excessive frequency. After fusing to the plasma membrane, the membrane from synaptic vesicles of the readily releasable pool is endocytosed. The endocytosed vesicles kind the recycling pool, which is scattered all through the synaptic terminal and which ultimately replaces the depleted readily releasable pool.
Mexico Weed (Castor). Zantac.
- Stimulating full-term labor in pregnant women.
- How does Castor work?
- Birth control.
- What other names is Castor known by?
- Constipation.
- Syphilis; arthritis; skin disorders; boils; blisters; swelling (inflammation) of the middle ear; migraines; softening cysts, warts, bunions and corns; promoting the flow of breast milk; and other conditions.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Dosing considerations for Castor.
- What is Castor?
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96863
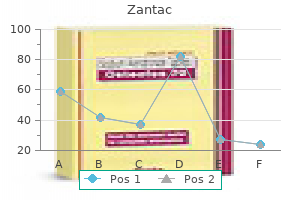
Buy zantac visa
Far extra dramatic examples of mass impact are when brain tissue not stays in its proper compartment. In such situations, a bit of the brain herniates or slips into a special compartment. Elevated stress within the anterior fossa is more probably to give rise to confusion and probably loss of consciousness. Depending on the degree of herniation, the midbrain, third cranial nerve, posterior cerebral artery, and superior cerebellar artery could additionally be compressed. This results from the herniated uncus compressing the third nerve because it exits the ventrum of the midbrain. Additional kinds of mind herniation may happen on their very own or together with other types. Central herniation, a type of transtentorial herniation like uncal herniation, is marked by parts of forebrain slipping beneath the tentorium at a site close to the midline. Tonsillar herniation is usually attributable to increased stress within the posterior fossa because of a tumor or hematoma. The tonsils of the cerebellum herniate down by way of the foramen magnum and press against the medulla and spinal wire. This is extremely dangerous as a end result of the pressure can interrupt connections critical to respiration and other critical functions. Finally, the most typical form of herniation is subfalcine, during which some portion of the cingulate gyrus slips underneath the falx. Although not at all times harmful or even symptomatic when occurring alone, a subfalcine herniation could additionally be a harbinger of more consequential damage. In different phrases, potential areas are precise fluid-filled areas solely underneath pathological conditions. Blood vessels traverse the meninges and might rupture into the potential areas both epidurally or subdurally. Epidural bleeds occupy the potential house between the unyielding cranium and the dura (B). Arterial vessels arrive from the periphery and penetrate the arachnoid and pia to provide oxygen and vitamins to the parenchyma. Venous blood is collected into sinuses formed by folds of dura and then emptied into the jugular veins that lead again to the heart. As blood travels in and out by way of the meninges, ripe alternative exists for blood to accidently leak into one of many potential or actual areas. Blood leaking out from cerebral vessels, due to trauma or different causes, is a probably life-threatening occurrence. The amassed blood or hematoma normally causes sudden symptoms, with the affected person complaining of a severe headache that arose explosively. The traits of bleeds in every of the four areas listed above are discussed in turn. The onset of signs, such as a lack of consciousness, may coincide with the onset of the epidural bleed or might observe a lucid interval, a interval with out signs during which blood presumably amasses to a dangerous and symptomatic level. It often follows a traumatic harm but can even happen spontaneously in elderly folks. A rupture of bridging veins is thought to be the most common cause of a continual subdural hematoma. Therefore, when the brain strikes inside its dural sack, the bridging veins are stretched. B: During vigorous shaking, particularly within the anterior-posterior axis, the mind moves throughout the dural sack. The bridging veins stretch and sometimes break at their thinnest point, between the arachnoid and the dura. Rupture of bridging veins is believed to be the most typical explanation for subdural hematomas.
Buy generic zantac from india
The resulting contraction of homonymous and synergist muscles opposes the original stretch. A minimum of anatomical details are illustrated in order to most clearly convey the essential circuitry. The endings of Ia afferents wrap around intrafusal fibers (if) and are activated by stretch. Ia afferents cross from the periphery into the central nervous system (dotted line) and directly contact -motoneurons that project into the periphery to innervate extrafusal fibers (ef) in the same or homonymous muscle, in addition to in synergist muscle tissue. The elementary stretch reflex circuit contains one central synapse, the synapse from the Ia afferent to an -motoneuron. The inhibition of antagonist muscles is accomplished through activation of the glycinergic Ia inhibitory interneuron (Ia ii). The members of an agonist�antagonist muscle pair move a joint in opposing directions. When a muscle is stretched and the homonymous muscle contracted, exercise in muscular tissues that oppose contraction of the homonymous muscle is inhibited. The Ia afferent-toinhibitory interneuron-to-antagonist motoneuron circuit is the basis for reciprocal inhibition. This pathway is disynaptic because it involves two synapses-the first between the Ia afferent and the inhibitory interneuron and the second between the inhibitory interneuron and the motoneuron. The inhibitory interneuron in this case is such an necessary cell that it has its personal name: the Ia inhibitory interneuron. Each leg alternates between support (solid blue and pink lines in the circle) and swing (dotted lines). For example, the left leg (red) begins the support section with a heel strike as the proper leg (blue) continues to be involved with the bottom. As the left leg assumes the weight of the physique, the right leg begins the swing section and so on. The immaturity of the gait is obvious in the minimal arm swing, the downward head posture, and fewer ankle flexion than is typically present in a healthy adult. The human determine in motion: An electro-photographic investigation of consecutive phases of muscular actions. In basic, the stretch reflex is strongest in muscular tissues that oppose gravity, termed physiological extensors, thus helping to keep postural control. The time period physiological extensor refers to muscles that, when contracted, oppose gravity, whereas the term physiological flexor denotes a muscle that works in live performance with gravity. According to this classification scheme, the quadriceps is a physiological extensor. Similarly, jaw-closing muscular tissues, such because the masseter or temporalis, elevate the jaw in opposition to gravity and thus are also physiological extensors, even though their activation decreases joint angle. Furthermore, these phrases are helpful as a end result of motor circuits are organized round physiological extensors and flexors quite than round joint extensors and flexors. To stay upright and to keep away from a permanently slack-jawed look, brainstem motor centers project to the spinal cord and tonically excite physiological extensors-not joint extensors (see Chapter 23). Thus, motor circuits respect a classification of muscular tissues in accordance with their work with respect to gravity. As defined earlier, exercise in -motoneurons leads to contraction of extrafusal fibers however not intrafusal fibers. In a slack configuration, no change in muscle length may be signaled by the spindle receptors. It is subsequently crucial that intra- and extrafusal fibers are the identical length always. When a motoneuron fires, the polar ends of the innervated intrafusal muscle fiber contract, which in flip stretches the equatorial area of the fiber. However, if an -motoneuron have been to be activated alone (B), the extrafusal fibers (ef) would contract however the intrafusal fibers would go slack. Consequently, Ia afferents would go "off-line" as they may now not sense stretch.

Buy zantac with paypal
Injection into dystonic muscle tissue reduces muscle spasm with out systemic side effects. Botulinum toxin injections are the therapy of selection for cervical dystonia, blepharospasm, spasmodic dysphonia, oromandibular dystonia, and limb dystonia, offering longterm benefit (with repeated injections) in 70�90% of patients. These neurotoxins block the discharge of acetylcholine on the neuromuscular junction by cleaving peptides required for vesicular membrane fusion, which selectively blocks cholinergic neurotransmission to striate and easy muscle tissue and temporarily paralyzes the injected muscles. Injections are also contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to botulinum toxin and albumin. Additionally, the teratogenicity of botulinum toxin has not been established, thus use in pregnant or lactating ladies is discouraged. Two of the seven serotypes present in nature are at present available commercially: sort A- onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox), abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport), incobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin); and sort B (Myobloc/NeuroBloc). When switching from one to another preparation of botulinum toxin, one should reference the product insert for typical conversion ratios. Botulinum toxin is a toxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. These neurotoxins block the discharge of acetylcholine at the Dystonia 67 neuromuscular junction by cleaving peptides required for vesicular membrane fusion, which selectively blocks cholinergic neurotransmission to striate and smooth muscular tissues and quickly paralyzes the injected muscles. Endocrine glands are additionally affected, lowering indicators for secretion of saved products. Ideal patients are these for whom expected benefits will outlast the inherent risks of the surgical process. Assessment of patients with isolated or mixed dystonia: an update on dystonia syndromes. Primary dystonia and dystoniaplus syndromes: medical characteristics, prognosis, and pathogenesis. For instance, a latent irregular posture underlying a tremordominant cervical dystonia could also be revealed by asking the affected person to loosen up with eyes close and let the head drift to the place that feels most comfy, which often demonstrates unrecognized torticollis or laterocollis. Ataxia manifests as disturbances of gait, expert movements, muscle tone, speech and eye movements, and is often as a end result of cerebellar dysfunction. The cerebellum is liable for the coordination of motor perform, and organizing the successive contractions of muscles into movement. The cerebellum is linked to a quantity of areas of the brain and spinal cord via feed forward and feedback loops and ensures coordinated actions by integrating motor and sensory inputs. Understanding the anatomy of the cerebellum and its connections is helpful in conceptualizing underlying pathology. The cerebellum is somatotopically organized, with the midline structures responsible for the trunk, head and eyes, and the extra lateral hemispheres controlling the limbs. Damage to the midline vermis will have an effect on posture and gait, and damage to the hemispheres will cause incoordination of the ipsilateral extremity. They are incessantly encountered together with different neurological and nonneurological indicators and symptoms. There are several deep cerebellar nuclei that obtain afferent fibers into the cerebellum. These nuclei include the dentate, which is the most important nucleus and receives the enter from the cerebellar hemispheres, in addition to the fastigial, emboliform, and globose nuclei. The fastigial nucleus receives enter from the vermis, and emboliform and globose nuclei from the paravermal zone. These nuclei then project back to the cerebellar cortex from which they obtained input. The enter and output tracts of the cerebellum could be simplified as follows: primarily efferent fibers out by way of the superior cerebellar peduncle, pontine fibers through the center cerebellar peduncle, and afferent fibers in through the inferior cerebellar peduncle. The classification of ataxic syndromes is subsequently inherently complex, Non-Parkinsonian Movement Disorders, First Edition. The precise number of particular person ataxias is unknown, but there are estimated to be at least 50 unique syndromes, and presumably as many as a hundred, each with distinct underlying causes. In an try and guide differential analysis, the ataxias have been break up into two major categories: sporadic or hereditary. The prevalence of ataxia of all causes is estimated at 60/100,000 within the United States, with 50/100,000 attributed to sporadic causes and 10/100,000 to hereditary ataxias. Though comparatively rare, the ability to acknowledge and precisely categorize the ataxias is a vital talent for the neurologist.
Order generic zantac pills
The enteric nervous system is in a position to operate nearly independently as a outcome of it consists of sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. This is in stark contrast to the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system, which only consist of preganglionic and postganglionic motor neurons. In addition, there are a mess of peptides, many of which have been first recognized in the intestine before eventually being discovered within the mind. Enteric neuropeptides include cholecystokinin, vasoactive intestinal peptide, neurotensin, bombesin, galanin, and substance P, all of that are additionally present within the mind. One inhabitants of enteric cells, the enterochromaffin cells, accommodates more than 95% of the serotonin discovered in the body! When excited by intraluminal stress, enterochromaffin cells secrete serotonin, which then initiates peristalsis. As could additionally be obvious from their different locations, these two plexi have completely different features. The myenteric plexus controls gut motility, and the submucosal plexus controls secretions into the lumen of the intestine. The vagus nerve innervates and has the best influence on actions of the esophagus and abdomen and little affect over intestinal and colonic motility. Sympathetic nerves innervate the decrease gastrointestinal tract and affect each motility and secretion. Other motility patterns embody mixing, the peristaltic rush that quickly propels noxious contents toward the anus, and the backward peristalsis that accompanies vomiting. The interstitial cell of Cajal is a pacemaker cell, meaning that it fires rhythmically on its own. It is the rhythmic discharge of the interstitial cell of Cajal that largely drives gut peristalsis. The commonest dysfunction of the enteric nervous system is Hirschsprung illness, also termed megacolon or congenital aganglionic megacolon. Hirschsprung illness results when neural crest cells fail to migrate into the distal colon. The severity of the disease varies, however it may be severe and demanding of immediate surgical intervention. The severity of the disease relies on how much of the colon is aganglionic, meaning lacking collections of enteric neurons. Newborns with this drawback present with constipation and are sometimes treated surgically. The normal part of the colon is pulled down and sewed over the aganglionic portion. Secretory reflexes of the enteric nervous system are responsible for returning about 9 liters-more than 2 gallons-of water to the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract each day. This is one pathway by way of which emotion, via an impact on sympathetic outflow, plays out in the motility of our guts, a typical expertise. Drowsiness also negatively impacts work performance and productiveness, increasing for instance, the variety of medical errors. Recently, Jerome Siegel and his colleagues studied three preindustrial groups of people and reported two particularly attention-grabbing findings. First, the folks studied slept for a median of just below 6 and 7 hours per night. This means that the fashionably prescribed 8 hours of sleep may not be a magical number or aim. Waking occurred throughout an lively vasoconstriction that coincided with the lowest temperature of the morning. These results recommend that sleep is timed to temperature changes that fashionable life has largely evened out. Hopefully, these data can be used to improve sleep among folks dwelling in industrialized situations. Depriving an animal or person from sleeping by preserving them awake will increase the strain to sleep, usually termed sleep drive. Extended sleep deprivation has serious adverse penalties, including demise if prolonged long sufficient.