Cabergoline dosages: 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg
Cabergoline packs: 4 pills, 8 pills, 12 pills, 16 pills, 24 pills, 32 pills, 48 pills, 56 pills
Order generic cabergoline on line
Renal anomalies, together with renal agenesis or hypoplasia, renal ectopia, horseshoe kidney, and hydronephrosis. The mewing cry, ascribed to irregular laryngeal development, becomes less pronounced with the References Lejeune J, et al: Trois cas de deletion partielle du bras courtroom du chromosome 5, C R Acad Sci [D] (Paris) 257:3098, 1963. Deletion 5P Syndrome Overhauser J, et al: Molecular and phenotypic mapping of the quick arm of chromosome 5: Sublocalization of the crucial area of the cri-du-chat syndrome, Hum Mol Genet three:247, 1994. Gersh M, et al: Evidence for a distinct region causing a cat-like cry in sufferers with 5p deletions, Am J Med Genet fifty six:1404, 1995. However, it could be very important notice that del 9p is heterogeneous and is related to variable deletion sizes. The candidate area for intercourse reversal, an occasional feature of deletion 9p syndrome, has been narrowed right down to the 9p24. Craniosynostosis involving the metopic suture resulting in trigonocephaly; flat occiput; short, upslanting palpebral fissures; epicanthal folds, prominent eyes secondary to hypoplastic supraorbital ridges; highly arched eyebrows; midfacial hypoplasia with a short nostril, depressed nasal bridge, anteverted nares, and lengthy philtrum; small mouth, micrognathia; posteriorly rotated, poorly formed ears with hypoplastic, adherent ear lobes; brief broad neck with low hairline. Long center phalanges of the fingers with extra flexion creases; short distal phalanges with quick nails; excess in whorl patterns on fingertips; foot positioning defects; simian crease. Ventricular septal defects, patent ductus arteriosus, and/or pulmonic stenosis in one third to one half of patients. Scoliosis, broadly spaced nipples, diastasis recti, inguinal and/or umbilical hernia, micropenis and/or cryptorchidism in males; hypoplastic labia majora in females. Onesimo R, et al: Chromosome 9 deletion syndrome and intercourse reversal: novel findings and redefinition of the critically deleted regions, Am J Med Genet 158A:2266, 2012. Chilosi A, et al: Del (9p) syndrome: Proposed habits phenotype, Am J Med Genet 100:138, 2001. A and B, Note the distinguished forehead with metopic ridge, trigonocephaly, frontal hair upsweep, short nostril with anteverted nares, and low-set ears. Although mental disability happens in nearly all of these patients, the severity of the clinical phenotype correlates with the extent of the triplicated material. Partial trisomy 9pterp21 is associated with gentle craniofacial options and rare skeletal or visceral defects. Partial trisomy 9pterp11 is related to the everyday craniofacial features, while partial trisomy 9pterq11-13 is related not solely with the typical craniofacial options but also with skeletal and cardiac defects. Partial trisomy 9pterq22-32 is associated with the everyday craniofacial options, intrauterine growth deficiency, cleft lip/palate, micrognathia, cardiac anomalies, and congenital hip dislocation. If the trisomic segment is bigger than that (9pter9q31 or 32), the scientific findings no longer match into the trisomy 9p syndrome but somewhat resemble trisomy 9 mosaic syndrome. Growth deficiency, primarily of postnatal onset; delayed puberty such that some patients continue to grow as much as the middle of their third decade. Microcephaly, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures, deep-set eyes, prominent nostril, downturned corners of the mouth, cup-shaped ears. Short fingers and toes with small nails and short terminal phalanges; fifth finger clinodactyly with single flexion crease; single palmar crease. Kyphoscoliosis, usually growing in the course of the second decade; hypoplasia of periscapular muscular tissues with deep acromial dimples; faulty ossification of the pubic bone, broad ischial tuberosity; pseudoepiphysis of metacarpals, metatarsals, and center phalanges of fifth fingers; delayed closure of cranial sutures and fontanels. Schinzel A: Trisomy 9p, a chromosome aberration with distinct radiologic findings, Radiology a hundred thirty:125, 1979. Pseudoepiphyses on metacarpals and metatarsals 2 to 5; notches on metacarpal 1, metatarsal 1, and proximal and middle phalanges of fingers; hypoplasia of the center phalanx of fifth finger, terminal phalanges of fingers, and middle and terminal phalanges of toes; thick epiphyses, particularly of terminal phalanges of big toe, thumb, and little finger; and clinodactyly of fifth finger. A�D, Note the ocular hypertelorism, prominent nose, downturned corners of mouth, cup-shaped ear, brief fingers, and 3-4 syndactyly. Surviving kids showed marked psychological deficiency and normally are bedridden with out the flexibility to talk. Individuals with dup10q25qter lack major malformations, and the prognosis is more favorable. Microcephaly; flat face with high forehead and excessive, arched eyebrows; ptosis; quick, downslanting palpebral fissures; microphthalmia; broad and depressed nasal bridge, anteverted nares, bow-shaped mouth with prominent higher lip; cleft palate; malformed posteriorly rotated ears. Camptodactyly, proximally positioned thumbs, syndactyly between second and third toes, foot place anomalies, hypoplastic dermal ridge patterns. Heart and renal malformations, every of which occurs in approximately one half of affected patients; kyphoscoliosis; pectus excavatum; 11 pairs of ribs; congenital hip dislocation; cryptorchidism.
Buy 0.25mg cabergoline overnight delivery
Hypoplasia with sparse, pale, fine hair to alopecia (61%); deficiency of eyelashes and eyebrows, pubic and axillary hair. The nails may be milky white in early childhood; later they thicken and separate from the nail bed. Connexins are membrane proteins which might be current in virtually all mammalian cells. Each connexin binds one other connexin in an References Joachim H: Hereditary dystrophy of the hair and nails in six generations, Ann Intern Med 10:400, 1936. Kibar Z, et al: the gene liable for Clouston hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia maps to the pericentromeric region of chromosome 13q, Hum Mol Genet 5:543, 1996. Renal failure is the commonest cause of demise and sufferers ought to be monitored carefully. Liver cystic illness occurs less generally than with Jeune thoracic dystrophy, one of many different ciliopathies. Sagittal craniosynostosis, dolichocephaly, frontal bossing, low-set easy ears, everted decrease lip, micrognathia. Fine sparse hair, extensively spaced tooth with decreased enamel, hypodontia, taurodontism and malformations of cusps, quick nails, lax pores and skin. Shortening of ribs and lengthy bones, notably the humeri and fibulae, flattened epiphyses of lengthy bones, delayed ossification of capital femoral epiphysis, convex higher and lower surfaces of vertebral bodies, pedicles of vertebral our bodies in lumbar region are quick with lower than normal widening of the interpedicular distance. Interstitial fibrosis of the kidneys with atrophic tubules and thickening of the tubular basement membrane indicative of nephronophthisis; liver cystic disease. Zaffanello M, et al: Sensenbrenner syndrome: A new member of the hepatorenal fibrocystic family, Am J Med Genet one hundred forty:2336, 2006. Lin A, et al: Cranioectodermal dysplasia: Comparison to Jeune syndrome and different ciliopathies, 2012, David W. Child at 12 months with sagittal craniosynostosis, frontal bossing, sparse hair, low-set cupped ears, epicanthic folds, redundant pores and skin folds and inguinal hernias. Child at 20 months (A) and at 3 years (B), with bitemporal narrowing, frontal bossing, sparse hair, low-set cupped ears, epicanthic folds, brief stature, redundant skin folds round ankles, and a repaired periumbilical incisional hernia. Radiographs of the arm exhibiting shortening of humerus, brachydactyly, and diffuse metaphyseal flaring (contributed by Angela E. Ocular manifestations rather than optic atrophy is a extra acceptable designation in that the latter has occurred in only one third of the sufferers. Autopsy specimens have proven interstitial fibrosis as properly as atherosclerotic adjustments in multiple organs. Skin biopsies have shown extreme atrophy within the epidermis with deposition of a hyaline material in the higher dermis, and hair follicle atrophy. An abnormal breakdown of extracellular parts brought on by decreased exercise of an unknown enzyme seems to underlie the pathogenesis of this condition. Mildly decreased delivery size; important postnatal progress deficiency becomes apparent between 6 months and 1 yr; delayed bone age. Frontal bossing; excessive forehead, prominent occiput; enlarged anterior fontanel with delayed closure; prominent scalp veins; periorbital swelling; drooping forehead skin; flat nasal bridge; anteverted nares; long philtrum, thick lips; large ears; micrognathia. Progressive optic atrophy; cataracts; exophthalmos; keratoconus; keratitis; glaucoma; horizontal nystagmus. Diminished scalp hair starting between 2 and three months with whole alopecia by 2 to 3 years; sparse eyelashes and eyebrows; extent of physique and facial hair variable. Failure of tooth eruption (pseudoanodontia) involving major and permanent dentition. Note the alopecia, excessive forehead, frontal bossing, periorbital swelling, drooping brow pores and skin, thick lips, massive ears, and micrognathia (A and B); the failure of tooth eruption (C and D); and the unerupted teeth (E). Oral leukokeratosis may be misdiagnosed as candida albicans and may trigger problem in sucking. Phenotype and genotype heterogeneity have proven this classification not to be particularly useful in predicting the phenotype or the related causal gene, and currently a more rational and helpful classification, based mostly on the mutated gene, is widely used. Progressive thickening, yellow-brown discoloration, pinched margins, and an upward angulation of distal ideas; the nails could finally be hypoplastic and even absent. Patchy to complete hyperkeratosis of palms and soles, callosities of toes, palmar and plantar bullae formation in areas of strain that are usually painful; keratosis pilaris with tiny cutaneous horny excrescences, particularly on the extensor surfaces of the legs and arms and on the buttocks; pilosebaceous cysts, together with steatocystoma and vellus hair cysts, epidermal cysts full of loose keratin on face, neck, and higher chest; verrucous lesions on the elbows, knees, and decrease legs; hyperhidrosis, particularly of palms and soles (50%). Leukokeratosis of mouth and tongue, especially in positions of increased trauma; scalloped tongue edge.
Buy generic cabergoline pills
Deficiency of postnatal onset, with brief trunk dwarfism becoming evident before 18 months. Platyspondyly, vertebral bodies show doublehumped look with central constriction, short neck, odontoid hypoplasia, scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis. Small ilia with irregularly calcified (lacelike) iliac crests in childhood developing into a marginal irregularity in adulthood; lateral displacement of capital femoral epiphyses; sloping, dysplastic acetabulae; wide pubic ramus. Restricted joint mobility; waddling gait; dislocated hips; genu valga and vera; rhizomelic limb shortening with irregular metaphyses and epiphyses; malformed olecranons and radial heads; broad hands and toes; short metacarpals, particularly the primary, and brief notched phalanges; cone-shaped epiphyses; small carpals. Spinal twine compression as a outcome of atlantoaxial instability is a preventable complication. Spranger J, Bierbaum B, Herrmann J: Heterogeneity of Dyggve-Melchior-Clausen dwarfism, Hum Genet 33:279, 1976. Dimitrov A, et al: the gene liable for DyggveMelchior-Clausen syndrome encodes a novel peripheral membrane protein dynamically associated with the Golgi equipment, Hum Mol Genet 18:440, 2009. Spondylometaphyseal dysplasia comprises a bunch of issues by which the spine and metaphyses of the tubular bones are affected. At least seven sorts have been categorized based mostly on minor radiographic differences and mode of transmission. Growth deficiency, particularly of trunk, with onset from 1 to four years of age; adult height, 129. Short neck and trunk with dorsal kyphosis; generalized platyspondyly with anterior narrowing in thoracolumbar area on lateral roentgenograms; on anteroposterior view, vertebral our bodies extend extra laterally to pedicles producing an "open-staircase" appearance; odontoid hypoplasia. Irregular rachitic-like metaphyses, especially the proximal femur with very short femoral necks; brief, stocky hands; hypoplastic carpal bones with late ossification (delayed bone age). A noticeably waddling gait with limitation of joint mobility turns into obvious at 15 to 20 months and References Kozlowski K, Maroteaux P, Spranger J: La dysostose spondylo-m�taphysaire, Presse Med 75:2769, 1967. Metatropic derives from the Greek word metatropos, which implies "changing patterns" and refers to the change in body proportions from short limb/long trunk to quick trunk/long limb as kyphoscoliosis becomes more progressive. There are multiple causes of the respiratory difficulties, together with abnormalities of the thorax, abnormal vocal cords with arytenoid fusion, and laryngotracheomalacia. The major reason for demise is cardiorespiratory failure attributable to kyphoscoliosis and the narrow thorax. All circumstances ranging from perinatal lethality to mild varieties are due to mutations of the identical gene. Birth weight normal; start length larger than 97th percentile; trunk, initially long relative to the limbs, turns into progressively brief with the development of kyphoscoliosis, leading to short-trunk dwarfism. Early platyspondyly with progressive kyphosis and scoliosis in infancy to early childhood; odontoid hypoplasia; delayed ossification/hypoplasia of the anterior portion of the first cervical vertebra, C1-C2 subluxation; slim thorax with brief ribs; quick limbs with metaphyseal flaring and epiphyseal irregularity with hyperplastic trochanters; distinguished joints with restricted mobility at knee and hip but increased extensibility of finger joints; irregular and squared-off calcaneal bones and precocious calcification of the hyoid and cricoid cartilage; erratic areas of microcalcifications in vertebral our bodies and epiphyses; hypoplasia of basilar pelvis with horizontal acetabula, short deep sacroiliac notch, and squared iliac wings. The trunk, initially long, turns into extremely short secondary to rapidly progressing kyphoscoliosis. Odontoid hypoplasia with C1-C2 subluxation can lead to cord compression, quadriplegia, and generally demise. Cervical References Fleury J, et al: Un cas singulier de dystrophie ost�ochondrale cong�nitale (nanisme m�tatropique de Maroteaux), Ann Pediatr (Paris) 13:453, 1966. Beck M, et al: Heterogeneity of metatropic dysplasia, Eur J Pediatr 140:231, 1983. Shohat M, et al: Odontoid hypoplasia with vertebral cervical subluxation and ventriculomegaly in metatropic dysplasia, J Pediatr 114:239, 1989. Kannu P, et al: Metatrophic dysplasia: Clinical and radiographic findings in eleven sufferers demonstrating long-term pure historical past, Am Med Genet 143:2512, 2007. Genevieve D, et al: Revisiting metatropic dysplasia: Presentation of a sequence of 19 novel sufferers and review of the literature, Am J Med Genet 146:992, 2008. Note the midface hypoplasia, giant joints, quick limbs, relatively large toes and arms, and congenital scoliosis. The term geleophysic (geleos, which means "pleased" and physis, that means "nature") refers to the happy-natured facial appearance typical of this disorder.
Purchase 0.5mg cabergoline overnight delivery
Managementissues Dietary cholesterol should be restricted and bileacid-absorbing resins can be used to sequester cholesterol from the enterohepatic circulation. The kidneys can turn into grossly enlarged and hypertension is often an associated characteristic. Glomerular filtration efficiency and co-occurrence of hypertension are additionally variable. On dental radiographs the tooth are seen to have bulbous crowns, roots narrower than regular and chambers and root canals that are small or utterly obliterated. The Shields classification acknowledges three varieties: � Type 1, associated with osteogenesis imperfecta; � Type 2, with no related bone defect; � Type three, much less extreme than Types 1 and 2, with no associated bone defects. Typically there are protuberances at the ends and juxta-epiphyseal areas of long bones, essentially the most regularly affected websites being the upper ends of the femurs and in addition the pelvis. There could be deformity of the legs, with genu valgum (knock knees) and Madelung-like deformity of the forearms. Onset is in early childhood and lesions continue to develop until closure of the epiphyseal plates. Bone overgrowth can cause peripheral nerve compression and cervical myelopathy (spinal twine injury). Approximately 10% of affected individuals develop profound sensorineural hearing loss across all frequencies. Otosclerosis is almost twice as frequent in females as in males, with distortion of sex ratio in patient sibships, implying prenatal choice operating against males. Management points the imply age of onset is within the third decade, 90% of affected individuals being underneath 50 years at prognosis. Recessive issues may be comparatively widespread, as heterozygous carriers can protect and transmit illness alleles without adverse choice. Night blindness, tunnel imaginative and prescient, pigmented areas in retina Albinism, oculocutaneous, sort 1 Phenylketonuria (see Chapter 8) Spinal muscular atrophy (see Chapter 8) Recessive blindness Congenital adrenal hyperplasia Masculinization of feminine genitalia, precocious puberty in males, salt deficiency (see Chapter 44) Medium-chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase deficiency Presents in early years with low blood glucose in response to an infection or starvation, inability to produce ketones (see Chapters 60�62) Gaucher disease In Ashkenazi Jews: (see Chapters 60�62) Smith�Lemli�Opitz syndrome Type 2 is deadly neonatally, with microcephaly, heart defect, renal dysplasia, cleft palate and polydactyly; Type 1 is much less extreme with psychological handicap, ptosis and genitourinary malformations (see Chapters 44, 60) Zellweger syndrome Peroxisome function disrupted, raised plasma levels of long chain fatty acids, extreme developmental delay, hypotonia, renal and hepatic failure (see Chapter 62) Classical galactosaemia Vomiting, hepatomegaly, jaundice and oedema. Recessive issues can be frequent in reproductively closed populations and molecular tests, if out there, can be used to establish unaffected carriers. The frequency of heterozygotes could be calculated from that of homozygotes by the Hardy�Weinberg legislation (see Chapter 30). You might level out that the frequency of carriers is as high as 1/25 amongst white folks, but that screening for the most common alleles that trigger cystic fibrosis is on the market each for him and any meant companion. Her father is an obligate heterozygote and the prospect his brother can be a service is half. Estimation of danger Recessive homozygotes are produced by three sorts of mating, although the primary of those is by far the commonest. Example: congenital deafness There are many (>30) non-syndromic, autosomal recessive types of congenital deafness that mimic one another on the gross phenotypic stage in that every one homozygotes are deaf (see Chapter 8). The main genetic consequence of inbreeding is to convey such recessive alleles to expression by growing the proportion of homozygotes. Children born to incestuous (parent�offspring or brother�sister) matings embrace around 40% with psychological defect and a lot of with impaired hearing or imaginative and prescient. At least 1100 million persons are both married to relatives as close as, or nearer than, second cousins, or are the progeny of such unions. Inbred people sometimes show decreased vigour, often identified as inbreeding despair. For instance, the offspring of first-cousin marriages have a barely increased danger of multifactorial disorder, 2. In outbred marriages recessive illnesses occur at one-quarter the square of their heterozygote frequencies (see Chapter 30) and common about 2% overall. Parent�childmatings With a mating between father and daughter (or mother and son), we want to consider whether allele e current in the daughter is inherited from her father or her mother. Strictly, all human beings are relatives, but for medical, legal and non secular causes we usually consider only members of our own, parental, grandparental, great-grandparental and descendent generations. The most distant relatives generally thought of with respect to consanguinity are second cousins. Incestuous matings are those between mother or father and child, or brother and sister and they contain the best risk.
Diseases
- Arachnodactyly
- Lobster hand
- Reticuloendotheliosis
- Hepatoblastoma
- Oral-pharyngeal disorders
- Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency
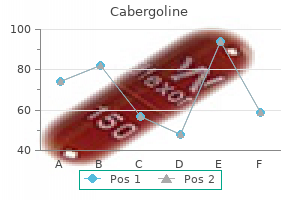
Order online cabergoline
Excretion is by tubular secretion and glomerular filtration, and 65�80% of a dose is excreted unchanged in the urine over 24 to forty eight hours, leading to high urinary concentrations. The 2 major metabolites, 10-N-glucuronide and 4-N-desmethyl olanzapine, seem to be inactive. About 57% of a dose is excreted within the urine, mainly as metabolites, and about 30% seems within the faeces. Antidepressants: fluvoxamine will increase focus of olanzapine; elevated focus of tricyclics. Anti-epileptics: antagonism (convulsive threshold lowered); carbamazepine increases metabolism of olanzapine; elevated risk of neutropenia with valproate. Antivirals: concentration decreased by ritonavir � consider increasing olanzapine dose. It is excreted within the urine and the bile as olmesartan; about 35�50% of the absorbed dose is excreted in the urine and the rest within the bile. The small amounts (1�2% of the dose or less) of intact olsalazine which may be absorbed are excreted primarily in urine. Unlikely that renal dysfunction will have any important effect on the kinetics of the drug. After reconstitution, chemically and physically stable for eight hours at 2�8�C and four hours at 30�C. Antifungals: absorption of itraconazole and ketoconazole reduced; keep away from with posaconazole; concentration elevated by voriconazole. Patients >65 years ought to all the time have the injection diluted for chemotherapyinduced nausea and vomiting. The metabolism of orlistat happens mainly within the gastrointestinal wall to kind two major inactive metabolites, M1 (4-member lactone ring hydrolysed) and M3 (M1 with N-formyl leucine moiety cleaved). Approximately 97% of the administered dose is excreted in faeces and 83% of that as unchanged orlistat. It is especially excreted in the urine as metabolites and small amounts of unchanged drug. Renal clearance exceeds glomerular filtration fee indicating that tubular secretion happens along with glomerular filtration. At least 75% of the oral dose reaches the systemic circulation because the carboxylate. A lower dose is required in extreme renal illness due to the energetic metabolite accumulating. Anecdotally a dose of 75 mg after each dialysis session has been used in haemodialysis sufferers without any issues. The pharmacokinetics and tolerability of oseltamivir suspension on haemodialysis and continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Platinum elimination is principally by renal excretion and tissue distribution; platinum metabolites primarily by renal excretion. By day 5, roughly 54% of the total dose was recovered in the urine and <3% in the faeces. Binds irreversibly to pink blood cells, which can extend the half-life of the drug. Pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin in sufferers with normal versus impaired renal perform. Antipsychotics: enhanced sedative results; danger of serious antagonistic results together with clozapine. Minor quantities (4% of the dose) are oxidised to a pharmacologically inactive metabolite. Oxcarbazepine is excreted within the urine primarily as metabolites; lower than 1% is excreted as unchanged drug. Oestrogens and progestogens: metabolism accelerated (reduced contraceptive effect). Oxprenolol is excreted mainly within the urine (almost completely in the type of inactive metabolites). Sympathomimetics: severe hypertension with adrenaline and noradrenaline (especially with non-selective betablockers) and probably with dopamine.
Cheap 0.25mg cabergoline with amex
Sucking and swallowing difficulties with frequent regurgitation lead to failure to thrive. Multiple infections, together with those of the respiratory, urinary, and gastrointestinal tracts, in addition to conjunctivitis and pores and skin and perineal abscesses happen. Infections with Candida and Pseudomonas, in addition to progressive cardiomyopathy, are the primary causes of early dying. No affected person has been able to stroll or purchase expressive language aside from babbling. Early therapy with beta-blockers might gradual the progression of cardiac deterioration. The instances with out mutations appeared to have longer survival and no cardiomyopathic manifestations. Vici syndrome is the first instance of a human multisystem dysfunction associated with defective autophagy. Profound cervicoaxial hypotonia with hyperextended neck posture, flexed lower limbs, and clenched fists. Agenesis of the corpus callosum and septum pellucidum, cerebral atrophy with enlarged ventricles, hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis and pons, gyral anomalies similar to heterotopias or different forms of non-lissencephalic cortical dysplasia, schizencephaly, delayed myelination, opercular hypoplasia, hypoplasia of optic nerves and chiasma. Postnatal onset microcephaly, ptosis, depressed nasal bridge, high palate, tented higher lip, delicate micrognathia. Congenital or acquired cataracts, hypopigmented retina and iris, hypoplasia of macula and optic disk, horizontal nystagmus, marked visible disturbance, lack of light reflex, inconsistent visual fixation and monitoring, slow or absent visible evoked potentials, photophobia. Hypopigmentation of the pores and skin, ranging from lighter complexion to complete albinism. Broad spectrum of defects starting from a combined immunodeficiency to an almost normal immunity. Miyata R, et al: Sibling instances of Vici syndrome: Sleep abnormalities and problems of renal tubular acidosis, Am J Med Genet A 143:189, 2007. McClelland V, et al: Vici syndrome associated with sensorineural listening to loss and proof of neuromuscular involvement on muscle biopsy, Am J Med Genet A 152A:741, 2007. Finocchi A, et al: Immunodeficiency in Vici syndrome: A heterogeneous phenotype, Am J Med Genet A 158A:434, 2012. Said E, et al: Vici syndrome-A rapidly progressive neurodegenerative disorder with hypopigmentation, immunodeficiency and myopathic changes on muscle biopsy, Am J Med Genet A 158A:440, 2012. There is marked generalized hypopigmentation relative to the ethnic background (E, F). Coarsening of facial options with full lips and macroglossia is famous in some older youngsters (G). The cardiac anomalies are normally not as severe as those with bilateral right-sidedness. The advanced cardiac anomalies, usually giving rise to cyanosis and early cardiac failure, are the major explanation for early demise. The possibility of gastrointestinal issues should also be considered, particularly as associated to the aberrant mesenteric attachments. Among other differences, the spleen dramatically reflects the variant laterality in the two. Left-right axis malformations are usually isolated however can occur as one function of a multiple malformation syndrome, the most typical of which is immotile cilia syndrome. As a result of faulty cilia and flagella, continual respiratory tract infections happen generally, and infertility in males, continual ear infections, and decreased or absent scent happen variably. The cilia are functionally abnormal and, on electron microscopy, have absent or irregular dynein arms connecting the nine pairs of microtubules. A subgroup of the immotile cilia Laterality Sequences 797 related to the asplenia. Tests to detect asplenia embrace analysis of pink blood cells for HowellJolly our bodies and Heinz bodies. As such, although normally sporadic, autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, and X-linked recessive inheritance have all been documented. At present, only 10% of cases are attributable to mutations of known genes, though additional candidate genes have emerged from research of left-right axis development in vertebrates. In the mouse, motile embryonic cilia generate directional move of extraembryonic fluid surrounding the node located on the tip of the embryo in the midline.
Purchase cabergoline 0.5mg mastercard
For comparability, mature small lymphocytes are current near the decrease left corners of each figures. C: the bone marrow biopsy is completely replaced by sheets of poorly preserved, malignant cells that display in depth crush artifact. These "double-hit" lymphomas, in addition to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, when confined to blood and marrow at the time of diagnosis, are simply misdiagnosed as precursor B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. This cervical lymph node specimen showed total effacement by a proliferation of enormous atypical lymphoid cells with prominent nucleoli and in affiliation with tangible body macrophages. An post-mortem lung from a affected person with lymphomatoid granulomatosis reveals extensive involvement with multiple necrotizing lesions. B: Lung biopsy exhibiting massive lymphoid cells restricted to blood vessels and displaying a vasculitic sample of involvement, with fibrinoid necrosis and angioinvasion. A and B: A supraclavicular lymph node biopsy reveals dense fibrous tissue and in depth coagulative tumor necrosis intimately related to sheets of large, malignant lymphoid cells. C: the malignant cells have giant, eosinophilic staining nucleoli (black arrow) and mitotic figures (white arrow). A: the biopsy of an belly mass exhibits, at low power, the basic "starry sky" look of rapidly proliferating malignant cells intermixed with bigger histiocytes actively engulfing tumor debris. B: Higher energy exhibits intermediatesized cells which are uniform in size and form, with multiple small basophilic nucleoli. This bone marrow biopsy demonstrates total replacement by quickly rising tumor cells, a few of which exhibit apoptosis admixed with "starry-sky" histiocytes engulfing tumor debris. This blood smear reveals L3-type lymphoblasts with multiple nucleoli and basophilic staining, vacuolated cytoplasm. The ideograms of chromosomes 8, 14, and the respective by-product chromosomes are to the left in color; the corresponding G-banded chromosome pairs are to the right. The tumor incorporates sheets of atypical plasmacytoid cells with a excessive mitotic fee. Gross lymph node specimens have been cut to present attribute homogenous pattern ("fish flesh" appearance) of a lymph node diffusely involved by continual lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (A), as in contrast with the nodular, heterogeneous look of a lymph node concerned with metastatic most cancers (B). Frequent smudged or "basket" cells, which are nuclear remnants of damaged cells, may be seen. B: Mantle cell lymphoma has small lymphocytes, condensed chromatin, and scant cytoplasm. C: Hairy cell leukemia has lymphopenia, ample cytoplasm with a central nucleus, and cytoplasmic projections. D: Splenic marginal zone lymphoma has lymphocytosis and irregular, eccentric nuclei. An inside mammary node is diffusely effaced by a proliferation of small, mature lymphocytes with excessive N:C ratios and condensed chromatin. Pale staining proliferation facilities are composed of prolymphocytes and immunoblasts-larger cells with vesicular nuclei and nucleoli. The lymph node is diffusely changed by small mature lymphocytes with high N:C ratios and condensed chromatin. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma; diffuse marrow involvement. A blood smear demonstrates mature lymphocytosis (A), and various magnified views of a marrow biopsy are shown (B�D). Diffuse infiltration includes full effacement of bone marrow architecture by sheets of lymphoma cells. D: Deletion of the p53 gene (red) at 17p13 as in contrast with a centromere 17 control (green). In this gross specimen, the spleen is homogeneously enlarged by diffuse infiltration of the purple pulp. For comparison, a traditional small lymphocyte is current within the upper left corner of the figure.
Purchase cabergoline paypal
Oculo-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum Oromandibular-Limb Hypogenesis Spectrum Pena-Shokeir Phenotype Schwartz-Jampel S. Chondrodysplasia Punctata, X-Linked Dominant Type Cleidocranial Dysostosis Cranioectodermal Dysplasia Craniometaphyseal Dysplasia Crouzon S. Geleophysic Dysplasia Mandibulofacial Dysostosis with Microcephaly Mucopolysaccharidosis I H, I H/S, I S Noonan S. Septo-Optic Dysplasia Sequence 808 304 588 270 312 756 118 500 194 714 546 540 7 426 736 748 202 246 one hundred fifty ninety two 776 164 424 eighty four 268 678 152 206 794 290 Occasional in Acrocallosal S. Albright Hereditary Osteodystrophy Aniridia�Wilms Tumor Association Blepharophimosis-PtosisEpicanthus Inversus S. Colobomata of Iris Frequent in Aniridia�Wilms Tumor Association (aniridia) Axenfeld-Rieger S. Chondrodysplasia Punctata, X-Linked Dominant Type Desbuquois Dysplasia Duplication 3q S. Atelosteogenesis, Type I Autosomal Recessive Chondrodysplasia Punctata Blepharophimosis-PtosisEpicanthus Inversus S. Chondrodysplasia Punctata, X-Linked Dominant Type Cleidocranial Dysostosis Costello S. Acrodysostosis Acromesomelic Dysplasia Amyoplasia Congenita Disruptive Sequence Apert S. Maxilla and Mandible Malar Hypoplasia Frequent in Atelosteogenesis, Type I Bloom S. Chondrodysplasia Punctata, X-Linked Dominant Type Ectrodactyly�Ectodermal Dysplasia�Clefting S. Hypoplasia of Nares and/or Alae Nasi Frequent in Cleft Lip Sequence Deletion 2q37 S. Mandibulofacial Dysostosis with Microcephaly Methimazole/Carbimazole Embryopathy Schinzel-Giedion S. Maxillary Hypoplasia, Often with Narrow or High-Arched Palate Frequent in Aarskog S. Mandibuloacral Dysplasia Mandibulofacial Dysostosis with Microcephaly Marden-Walker S. Mucopolysaccharidosis I H, I H/S, I S Mycophenolate Mofetil Embryopathy Nablus Mask-Like Facial S. Chondrodysplasia Punctata, X-Linked Dominant Type Diastrophic Dysplasia Distichiasis-Lymphedema S. Oral Region and Mouth Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate Frequent in Amnion Rupture Sequence (disruptive) Branchio-Oculo-Facial S. Mucopolysaccharidosis I H, I H/S, I S Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia, Type 2B Neu-Laxova S. Microstomia fifty four 578 372 752 168 376 718 600 704 658 282 338 576 88 106 776 596 690 238 268 134 24 332 one hundred sixty 374 156 164 Frequent in Deletion 9p S. Linear Sebaceous Nevus Sequence Mandibulofacial Dysostosis with Microcephaly Marfan S. Meningomyelocele, Anencephaly, Iniencephaly Sequences Microcephalic Primordial Dwarfing S. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia, Type 2B Oculo-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum Oral-Facial-Digital S. Oral Frenula (Webs) Frequent in Chondroectodermal Dysplasia Oral-Facial-Digital S. Microglossia Frequent in 488 352 836 244 Oromandibular-Limb Hypogenesis Spectrum 836 Occasional in Occasional in Frontonasal Dysplasia Sequence Mohr S. Teeth Anodontia (Aplasia) Frequent in Albright Hereditary Osteodystrophy Axenfeld-Rieger S. Chondroectodermal Dysplasia Cleidocranial Dysostosis Ectrodactyly�Ectodermal Dysplasia�Clefting S. Enamel Hypoplasia Frequent in Albright Hereditary Osteodystrophy Cleidocranial Dysostosis Cranioectodermal Dysplasia Goltz S.