Aristocort dosages: 40 mg, 15 mg, 10 mg, 4 mg
Aristocort packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills

Purchase aristocort line
Treatment for bronchial asthma manifesting as cough is similar as the remedy for asthma. In general, however, the defective gene product leads to the long-observed clinical manifestations of the disease, including thick, viscid mucus in the tracheobronchial tree, leading to purulent bronchiolitis and bronchitis with subsequent bronchiectasis, pulmonary fibrosis, and respiratory failure; pancreatic duct obstruction, leading to pancreatic insufficiency with steatorrhea and failure to thrive; and abnormally excessive sweat chloride and sodium concentrations. Other organisms, similar to Burkholderia cepacia, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Alcaligenes xylosoxidans, Aspergillus fumigatus, or nontuberculous mycobacteria can also seem; their significance remains undetermined. The most common presenting symptom is cough, which may appear throughout the first weeks of life or could also be delayed for decades. Furthermore, in atypical instances, patients could not have pancreatic insufficiency (~10% of patients) and thus may not reveal steatorrhea and failure to thrive. There is a few relationship between the diploma of pulmonary disease severity and the diploma of digital clubbing. The proper method is to use quantitative analysis of the concentration of chloride within the sweat produced after pilocarpine iontophoretic stimulation. Chloride concentrations greater than 60 mmol/L are considered optimistic, and people lower than forty mmol/L are unfavorable (normal). Healthy adults have slightly greater sweat chloride concentrations than do kids, however the identical pointers maintain for positive exams in adults. Newborns within the first few weeks of life might not produce a large enough quantity of sweat to analyze (75 mg minimum), but in those that do (the majority), the outcomes are correct. Definitive testing with the sweat chloride take a look at needs to be carried out on infants with optimistic screening outcomes. Several research have proven survival to be considerably better in center-based care than in non�center-based care. Vascular rings and slings are often associated with inspiratory stridor as a outcome of the irregular vessels compress central airways, mostly the trachea (see Chapter 3). The analysis may be suspected from plain radiographs of the chest, especially these showing tracheal deviation and a right-sided aortic arch. Further help for the analysis could be discovered at bronchoscopy (which shows extrinsic compression of the trachea or a major stem bronchus), barium esophagram (which exhibits esophageal compression), or each. The definitive analysis is made with computed tomographic angiography or magnetic resonance angiography. The chest radiograph usually reveals a density in the left decrease lobe; this density often seems to contain cysts. The feature distinguishing a sequestered lobe from a complicated pneumonia is that the blood provide arises from the aorta and never the pulmonary circulation. They manifest in infancy with respiratory distress in almost 50% of circumstances; the opposite half could manifest as cough with recurrent infection later in childhood and even maturity. Radiography exhibits localized overinflation, typically dramatic, with compression of adjoining lung tissue and sometimes atelectasis of the contralateral lung due to mediastinal shift away from the involved facet. Bronchoscopy can document patent bronchi and may in all probability be performed in older children in whom congenital lobar emphysema could be confused with acquired overinflation of a lobe as the result of bronchial obstruction, as with a overseas physique. Tracheoesophageal fistula is common, with an incidence of about one in 5000 reside births. Of these fistulas, the massive majority (85%) are associated with esophageal atresia; solely 3% are the isolated, H-type fistula (a patent esophagus with fistulous tract connecting the esophagus and trachea). A neonate with esophageal atresia experiences respiratory distress, excessive drooling, and choking and gagging with feeding. The H-type fistula causes more delicate signs and may be undiagnosed for months or even years. In the older baby with H-type fistula, a barium esophagogram could or may not reveal the fistula. Bronchoscopy and esophagoscopy ought to allow direct visualization of the fistula; nonetheless, the opening could also be hidden in mucosal folds. Many children born with tracheoesophageal fistula have recurrent cough and decrease respiratory tract an infection for a number of years, even after successful surgical correction. The cough is characteristically the harsh cough of tracheomalacia, which is current at the site of the fistula. Hemangiomas may be present inside the airway and might cause cough, not often with hemoptysis. Stridor (if the hemangioma is high in the airway) and respiratory misery (if the hemangioma is large) can also occur. In rare instances, with very giant airway hemangiomas, there could even be dysphagia from extrinsic compression.
Order 4mg aristocort mastercard
Many of these risks exist for transfusion recipients of any age, whereas others pose a greater risk to the neonatal recipient. Parents must be advised of the dangers, advantages, and alternatives to transfusion, and informed consent should be documented within the medical document together with the indications for, and results of, the prescribed transfusion. Previously irradiated and stored (24 hours) items may have plasma K+ unsafe for large-volume transfusion to neonates, particularly if administered rapidly. Therefore, they need to be issued instantly post-irradiation, or washed or volume-reduced to take away extracellular K+ that accumulates after processing. These embrace hemolysis from shear and/or heat stress imposed on erythrocytes by extracorporeal circuits, infusion units, filters, blood heaters, or phototherapy gentle exposure. When a hemolytic transfusion reaction is suspected, the transfusion ought to be immediately stopped, blood cultures (from affected person and blood component(s)) should be obtained, and the transfusion service should be notified. Mannitol could also be administered to drive diuresis, however osmotic diuresis in neonates is controversial due to concerns about alterations in cerebral microcirculation and threat of intraventricular hemorrhage. These reactions are believed to end result from the discharge of pyrogenic cytokines by leukocytes within the plasma during storage. Because of the immaturity in neonatal liver and kidney function, and the low quantity of skeletal muscle mass, transfusion of citrate-enriched blood may end up in hypocalcemia from citrate toxicity. The quantity of citrate infused right into a neonate during a small-volume transfusion (10-15 mL/ kg) is very unlikely to trigger hypocalcemia; nonetheless, the citrate load during an exchange transfusion can reach very excessive ranges and lead to symptomatic hypocalcemia. In a retrospective review of 106 infants undergoing one hundred forty trade transfusions, symptomatic hypocalcemia was one of the most frequent serious side effects. Eighty-one infants had been categorised as "wholesome" if indication for trade was solely asymptomatic hyperbilirubinemia; 25 infants have been categorized as "unwell" if co-morbid situations existed. Notifying the transfusion service for further laboratory evaluation of the response is essential to properly classify the response so that the affected person could be managed appropriately. For mild or localized cases, transfusion can be continued once symptoms have subsided; however, extreme allergic reactions (anaphylactoid or anaphylactic reactions) could require therapy with corticosteroids and/or epinephrine. The same blood unit should by no means be restarted in extreme instances, even after symptoms have abated. In these instances, IgA-deficientlasma products may be obtained, however require the utilization of uncommon donor registries. Prolonged latency of scientific manifestations and death is believed to result from thymic and/or extrathymic semi-tolerance for allogeneic cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Fortunately, this complication may be prevented by pretransfusion gamma irradiation of mobile blood parts at a dose of 2. Many transfusion providers irradiate all cellular blood merchandise given to preterm infants born weighing 1. The known and presumed indications for irradiation of blood components for neonates are listed in Box 89-1. Treatment is mainly supportive, together with fluid and/or vasopressor support in the face of hypotension. These antibodies activate and sequester recipient neutrophils throughout the endothelium of the lungs, finally leading to the manufacturing of vasoactive mediators and capillary leak. Transfusion of adult blood products containing plasma with naturally occurring anti-T antibodies into neonates with T-activation can current with intravascular hemolysis following transfusion, or unexplained failure to achieve the anticipated post-transfusion hemoglobin increment. Alternatively, T-activation may be detected within the laboratory with none evidence of scientific hemolysis, making broad-based screening impractical. T-activation has been reported primarily in neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis, especially in these with extreme illness requiring surgical intervention but in addition in septic infants with other surgical problems. Those infants with T-activation had Clostridia cultured from blood, peritoneal fluid, or stool in 14 of 16 (88%) of circumstances and have been extra more likely to have intestinal perforation at laparoscopy. Infants with discrepancies in forward and reverse blood typing and proof of hemolysis on smear ought to be suspected of T-activation. The prognosis is confirmed by particular agglutination tests using peanut lectin Arachis hypogea and Glycine soja. Severity and treatment can range from full recovery with conservative medical management to intestinal perforation and bowel necrosis requiring surgical intervention. Some hypothesize that even delicate reductions in blood circulate and subsequent reperfusion occurring in response to hypoxia may contribute to bowel damage. Infection results in neuroinvasive illness (meningo-encephalitis, spastic paralysis) in roughly 20% of individuals, with extra extreme sequelae within the elderly and immunocompromised. Despite extensive donor screening and laboratory testing, infections can still be transmitted through blood merchandise.
Aristocort 4 mg on line
Multiple events occurring over the course of the day of presentation escalate concern for severe infections and child maltreatment. Clinical suspicion of kid maltreatment additionally increases the probability of future antagonistic events. The historical past ought to concentrate on the activities and behaviors preceding the occasion, traits of the episode itself, interventions performed and their effect, and post� episode occasions and habits. A complete past medical history, social history, and family history should also be obtained for figuring out clues which will help in narrowing the main target of the investigation. Key historical findings by system can be useful in narrowing the differential (see Table 5. The location and position of the kid prior to the occasion also wants to be famous, such as placement in a automobile seat, on a gentle or firm floor, inclined or supine, and with or without surrounding blankets or pillows. Infants should bear an entire head-to-toe examination fully unclothed, including vital indicators with pulse oximetry, development parameters with head circumference, and full ear, nostril, throat, cardiac, respiratory, stomach, neurologic, musculoskeletal, and pores and skin examinations. Any abnormalities on the presenting examination might point out varied attainable diagnoses and will prompt extra analysis for the advised etiology (see Table 5. Abnormal progress parameters might establish failure to thrive, which can be suggestive of pathologic reflux, cardiac illness, or metabolic disorders. Signs of trauma, together with retinal hemorrhages, unexplained bruising, or proof of oral pharyngeal trauma (torn frenulum) suggestive of child maltreatment should also be noted. Abnormality of the neurologic examination should be absolutely assessed, with concern for intracranial bleed or mass requiring immediate attention. However, any regarding historical or physical options require the need for further in-patient evaluation performed in a targeted manner based on the scientific presentation and suspected analysis (see Table 5. Some infants will present with overt symptoms similar to coughing, choking, and laryngospasm following regurgitation. Others can present with out visible regurgitation but quite with posturing including arching of the back, torsion of the neck, and lifting up of the chin. This phenomenon, often identified as Sandifer syndrome, could be scary to the observer and is usually confused with seizure activity. Patients who current with these circumstances will sometimes have extra historical and examination findings to recommend their underlying etiology. Patients with intussusception can have sudden and severe belly ache, inconsolable crying, and drawing up of the legs to the stomach. The classic presentation of intussusception is the triad of abdominal pain, a sausage-shaped belly mass, and currant-jelly stool. Similarly, infants with volvulus can present with sudden onset abdominal pain accompanied by emesis. When testing is taken into account, it is important to perceive the utility of assorted modalities. A history of a quantity of events on the day of presentation is related to an infectious etiology. Additional historic clues include current fever, irritability, altered level of arousal, cough, or coryza. Physical examination findings may affirm the suspicion of an infectious etiology, while hypothermia and sick look at presentation ought to result in concern for more severe infectious etiologies. Apnea could be the presenting symptom of viral decrease respiratory tract infections, with the telling signs of coryza and cough delayed by hours to days. Neonates with pertussis could present with or develop few different symptoms, so a cautious history of potential exposure is essential for early analysis. Although eighty Section 1 RespiratoryDisorders unusual in infants, sturdy suspicion or the event of a staccato cough with posttussive emesis, or a classic "whoop," ought to prompt treatment whereas ready applicable testing. A historical past of irritability and/or altered stage of arousal could counsel a serious infection. Paradoxical irritability (crying when held) suggests gentle tissue or bone an infection or a fracture. Examination findings of concern embrace ill appearance, fever, hypothermia, lethargy, nuchal rigidity, and poor peripheral perfusion. The infection can lead to cardiorespiratory compromise, which can manifest as apnea, shade change, altered ranges of consciousness, or change in muscle tone. Thus the dearth of this historic fact should elevate the suspicion for seizure within the differential.
Discount aristocort online mastercard
The cardiac cycle begins with atrial systole, the sequential activation and contraction of the 2 thin-walled higher chambers. Atrial systole is followed by the delayed contraction of the extra powerful lower chambers, termed ventricular systole. Isovolumic contraction: the brief interval of early contraction when the strain builds inside the ventricle however has but to rise sufficiently to permit ejection 2. Ventricular ejection: when the ventricles eject blood to the body (via the aorta) and to the lungs (via the pulmonary artery) three. Isovolumic leisure: the interval of ventricular relaxation when ejection ceases and stress falls inside the ventricles During ventricular contraction, the atria chill out (atrial diastole) and obtain venous return from both the physique and the lungs. Then, in ventricular diastole, the decrease chambers relax, permitting initial passive filling of the thick-walled ventricles and emptying of the atria. This atrial systole augments ventricular filling just before the onset of the subsequent ventricular contraction. The relationship of blood quantity, stress, and flow determines opening and closing of coronary heart valves and generates attribute heart sounds and murmurs. The proper atrium and right ventricle are located anteriorly, immediately beneath the sternum. The outflow tract of the right ventricle, which accommodates the pulmonary valve, rises to the left of the sternum. The parts of the left aspect of the heart which are close to the chest wall embody the left ventricular apex and the ascending aorta because it passes up to the best of the sternum. The quantity of pressure that forces the valve closure influences the depth of a coronary heart sound. Other mechanical elements corresponding to valve stiffness, thickness, and tour have less impact on sound intensity. The quantity of turbulence and consequently the depth of a cardiac murmur is directly proportional to both the pressure difference or gradient across a narrowing or defect and the blood move or volume shifting throughout the site. As sound radiates from its source, sound depth diminishes with the square of the gap. Sound passage through the physique is affected by the transmission traits of the tissues. Fat has a more pronounced dampening effect on higher frequencies than does more dense tissue corresponding to bone. If the difference in tissue density is significant-for example, between the center and lungs-more sound vitality is misplaced. Only the loudest sounds may be heard when lung tissue is positioned between the center and chest wall. In distinction to depth, the frequency of a cardiac murmur is proportional to strain difference or gradient across a narrowing alone. The majority of significant structural congenital heart disease is acknowledged in the first few weeks of life. The age at recognition or referral often dictates the character of the cardiac anomaly and the urgency with which assessment is important. Preferentially, circulate is directed throughout the foramen ovale to enter the left atrium and, subsequently, the left ventricle. Other and more complicated lesions (forms of heterotaxy) together characterize 5-10% of all lesions. The pressures inside each ventricles are essentially equal, inasmuch as each chambers pump to the systemic circulation. However, in utero, the best ventricle does the majority of the work, pumping 66% of the mixed cardiac output. Through mechanical and chemical mechanisms, the ductus arteriosus begins to close. Intermittent right-to-left atrial level shunting through the foramen ovale may occur, significantly if pulmonary vascular resistance fails to drop.
Aristocort 4mg for sale
Secretory diarrhea is the outcomes of both impaired absorption of NaCl from villous enterocytes or increased chloride secretion from crypt cells, secondary to exogenous toxins from micro organism or viruses or endogenous substances (hormones, neurotransmitters, or cytokines), or from inherent defects in the sodium or chloride channels. Osmotic diarrhea outcomes from nonabsorbable substances in the intestinal lumen, which will increase the osmolality of the luminal contents. This ends in both retention of fluid or secretion of fluid into the intestinal lumen, therefore resulting in diarrhea. In distinction to secretory diarrhea, typically osmotic diarrhea improves with fasting. Osmotic diarrhea may be distinguished from secretory diarrhea by measuring the electrolyte concentration in the stool and the osmotic hole. Some diarrheal problems could have a secretory and osmotic element, as is usually seen in celiac disease. Although diarrhea alone may be liable for an increase in fat excretion of up to eleven g per day (normally, <7 g fat/day is excreted by individuals consuming a hundred g fat/day), when larger quantities of fat are found in the stool the patient must be evaluated for a dysfunction of fats absorption. Based on the outline of diarrhea as osmotic or secretory or mixed osmotic and secretory parts, infantile diarrheal etiologies could be distinguished, as shown in Box 92-1. Disorders of Carbohydrate Absorption the enterocytes within the small gut have at their apical floor brush border various enzymes liable for the digestion of carbohydrates. Patients with carbohydrate malabsorption issues, whatever the cause, current with extreme watery diarrhea, which results from osmotic motion exerted by the malabsorbed oligosaccharide4 (lactose, sucrose, or glucose) within the intestinal lumen. The malabsorbed sugars are then fermented by colonic micro organism, producing a mixture of gases. Congenital sucrase-isomaltase deficiency is attributable to lowered activity of the comb border enzyme sucrase-isomaltase. Patients present with diarrhea, usually observed across the age of three to 6 months when the toddler is weaned from breast milk to child meals that contain sucrose. Affected infants present with severe, persistent or intermittent watery diarrhea, belly distention, cramping, metabolic acidosis, and failure to thrive. A detailed historical past will provide the correlation of the onset of diarrhea and the dietary modifications. Stool osmolality reveals an elevated osmolar hole (>50 mOsm), indicating the presence of malabsorbed sugars. Congenital lactase deficiency may be identified by obtaining an excellent dietary historical past and may be demonstrated by an absence of improve in blood sugar after a load of lactose. When handled appropriately the sufferers have good catch-up growth with normal psychomotor development. Maltase-glucoamylase is very comparable to sucrase-isomaltase (59% homology), and has two catalytic websites that are equivalent to these of sucraseisomaltase. The clinical symptoms are similar to different disaccharidase deficiencies with diarrhea, abdominal distention, and bloating. Endoscopy with biopsies will present decreased ranges of the enzyme when symptomatic remedy requires starch elimination from the food plan. The babies usually present very quickly after birth with watery diarrhea, vomiting, poor weight gain, lactosuria, aminoaciduria, and adjustments within the nervous system. Congenital lactase deficiency is brought on by the deficiency of lactase, within the small gut and has been linked to chromosome 2q21. Usually, congenital lactase deficiency is an isolated deficiency, but Nichols and colleagues have reported it in association with other disaccharidase deficiencies such as maltase-glucoamylase. Breast milk and different commercial formulas have lactose; subsequently, the onset is usually within the first 10 days of life. The diarrhea resolves after switching to a lactose-free method,9 which confirms the diagnosis. Apart from diarrhea, these infants are vigorous and have an excellent appetite; they exhibit poor weight acquire however no vomiting. Infants current in the neonatal interval with severe watery diarrhea, which can result in fast dehydration and death. These infants present firstly of breastfeeding or ingestion of glucose-containing formulation with extreme watery diarrhea that usually may be confused with urine. The predominant sugar of breast milk is lactose, which is hydrolyzed to glucose and galactose earlier than being absorbed.
Syndromes
- Medicine to reverse the effect of the narcotic (narcotic antagonist)
- Fluids by IV
- Bowel problems, such as gallstones, intestinal obstruction, and rectal prolapse
- Stress of unfamiliar environment
- The entire penis looks red and swollen
- Certain medications that significantly reduce heart function or blood pressure
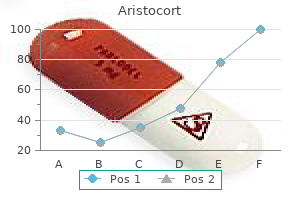
Order aristocort with a mastercard
When these two situations are mixed with a usually externally rotated hip from a decent posterior hip capsule, they produce a very externally rotated or out-toed position. They are categorized according to the direction of angulation-posteromedial or anterolateral. Posteromedial angulation is much less frequent but is characterised by spontaneous decision with progress and growth. Anterolateral angulation is extra frequent and is often related to different underlying congenital abnormalities, similar to congenital absence of the fibula. Posteromedial angulation has three associated clinical issues: angular deformity, the calcaneovalgus foot, and size discrepancy of the decrease extremities. The angular deformity happens on the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the shafts. The degree of angulation varies between 25 and sixty five levels and is equal in each posterior and medial directions. The explanation for congenital posteromedial angulation in the tibia and fibula is unknown. Posteromedial angulation resolves with development, especially through the first 3 years of life. The posterior bowing tends to resolve extra rapidly than the medial bowing, which may not resolve till 5 years of age. However, the related shortening of the tibia and fibula persists and progresses throughout development. The look of the foot also improves, although a pes planovalgus appearance could persist. The most common sequela of posteromedial angulation is a discrepancy in leg length. An appropriately deliberate epiphysiodesis (physeal closure) of the longer limb is the commonest process. Careful clinical and radiographic analysis is critical to set up the right analysis. Congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia is typically associated with neurofibromatosis. Whether the hip stabilizes, subluxates, or finally dislocates is determined by postnatal factors. Most developmental dislocations are postnatal in origin; nevertheless, the precise time of their incidence is controversial. Neonatal hip dislocations are classified into two main teams: the everyday, which is present in a neurologically regular toddler, and the teratologic, which is present in an toddler with an underlying neuromuscular dysfunction, such as myelodysplasia, arthrogryposis multiplex congenita, or a fancy of syndromes. Teratologic dislocations occur in utero and are, therefore, actually congenital in origin. The genetic components embody a constructive family history (20%) and generalized ligamentous laxity, an inherited trait. The physiologic components embody female predominance (9: 1) and maternal estrogen and other hormones related to pelvic leisure during labor and delivery. The mechanical components embody primigravida, breech presentation, and postnatal positioning. Positioning has a big impact in figuring out which hip stabilizes and which can progress to dislocation. The maternal estrogen and other hormones related to pelvic leisure at supply cross the placenta and end in additional, albeit momentary, relaxation of the newborn hip joint. Decreased hip motion leads to the dearth of normal stimulation for the growth and improvement of the cartilaginous acetabulum. The presence of either of these situations necessitates a careful examination of the hips. These positions put the unstable hip beneath irregular pressure on account of the normal hip flexion and abduction contractures. Consequently, an unstable femoral head may be displaced from the acetabulum over several days and even weeks. TheOrtolanisign,orclickofreduction,iselicitedwhen abducting the hip on this manner. It has been estimated that approximately 1 in 100 newborns has a clinically unstable hip.
Purchase aristocort 4mg overnight delivery
Comparing alloimmunization in preterm infants after transfusion of fresh unmodified versus stored leukocyte-reduced pink blood cells. Is there a job for autologous/placental pink blood cell transfusions within the anemia of prematurity Thomsen-Friedenreich activation in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis in Taiwan. Neurodevelopmental end result of extraordinarily low delivery weight infants randomly assigned to restrictive or liberal hemoglobin thresholds for blood transfusion. A systematic evaluation of the impact of temperature on coagulation enzyme activity and platelet function. Reduction in potassium focus of saved red blood cell units using a resin filter. Many necessary secondary features are also carried out, such as the endocrine operate of the pancreas. In fact, what was once thought of a simple system of digestion and absorption is now recognized as one thing much more complex and dynamic. This locations the extra demand of getting mechanisms in place to defend the host from toxins and pathogens. It is exceptional that this tube, open to the surface world at each ends and colonized by micro organism for a good portion of its length, is tolerated so properly and has relatively few complications associated with it. But troubles do occur, and in the neonate, most may be traced to developmental anomalies. The Beginning During gestation, the alimentary canal may be merely thought of because the folding of endoderm and splanchnic mesoderm into a tube on the end of week 3 and the beginning of week 4. Shortly thereafter, the caudal portion of the yolk sac turns into enclosed and varieties the hindgut. The midgut resides between the foregut and the hindgut, near the yolk sac, which stays outdoors the embryo. The midgut stays in communication with the yolk sac till the yolk stalk closes through the 10th week of gestation. Initially the digestive tube ends blindly-cranially at the oropharyngeal membrane and caudally at the cloacal membrane. These membranes, made up of endoderm and ectoderm, break down, with the oropharyngeal going first at the start of week 4 followed by the cloacal at the start of week 6. Rather, it serves as a conduit between mouth and abdomen and, at the gastroesophageal junction, capabilities to keep away from reflux of stomach contents back up the esophagus. Although this task sounds simple, the esophagus performs its roles so well that no esophageal substitute has been found that 1364 does anyplace close to as good a job. All efforts are made to maintain a native esophagus, even a severely compromised one, rather than go together with any substitute. The totally developed esophagus extends from the pharynx and cricopharyngeal sphincter within the neck to the decrease esophageal sphincter and gastroesophageal junction in the abdomen. The higher esophagus is equipped by branches descending from the inferior thyroid artery. The center and lower thirds of the esophagus are supplied by branches arising instantly from the bronchial vessels or the descending thoracic aorta. The stomach and lower esophagus additionally receive blood supply from the left gastric and inferior phrenic arteries. The esophagus varies in size from thirteen to 25 cm depending on the age and height of the patient. There are 4 areas of pure anatomic constriction of the esophagus: (1) on the stage of the cricopharyngeal sphincter, (2) as the aortic arch crosses anteriorly, (3) because the left major stem bronchus crosses anteriorly, and (4) at the stage of the decrease esophageal sphincter. Foreign bodies within the esophagus are most likely to lodge at one of these areas of constriction, and burns from caustic ingestion are probably to be more severe in these areas. The esophagus is differentiated from the primitive foregut through the fourth week of gestation. The septum remains at about the same stage in the fetus while the physique grows cranially. This leads to elongation of the esophagus, primarily from "ascent" of the pharynx somewhat than "descent" of the abdomen. It reaches its full length, relative to the dimensions of the creating fetus, in the course of the seventh week of gestation. Aberrations throughout this section of improvement lead to esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistulas. The lumen of the esophagus is nearly obliterated during the seventh and eighth weeks of gestation, secondary to rapid proliferation of mucosal epithelial cells.
Order aristocort 4mg fast delivery
In certain types of hypothyroidism, similar to iodine-deficient cretinism, the preferential synthesis of T3 might occur. Retardation of bone maturation is current in about half of the newborns with primary hypothyroidism and should counsel the fetal age at which a deficiency developed in the supply of thyroid hormone to responsive tissues. Retardation of bone maturation in neonates is best assessed by radiographs of the knee and foot. The ossification facilities of the calcaneus and talus seem at about 26 to 28 weeks of gestation, and people of the distal femur at about 34 to 36 weeks. Absence of the distal femoral epiphyses in a new child weighing 3000 g or extra or absence of the distal femoral and proximal tibial epiphyses in an toddler weighing 2500 to 3000 g at delivery suggests an intrauterine thyroid hormone deficiency. Ossification of the cartilage of the epiphyses can be disturbed in hypothyroidism. Ossification normally begins from the center of the cartilage and extends peripherally in an orderly method. In hypothyroidism, calcification of epiphyseal centers starts from a quantity of irregular foci scattered within the creating cartilage. This finding is extremely attribute of hypothyroidism and offers a powerful clue for the diagnosis. Abnormal modifications happen in the epiphyseal cartilage secondary to thyroid hormone deficiency earlier than calcification, so even after hypothyroidism is treated, the characteristic pattern of calcification seems in all of the facilities that usually would have calcified in the course of the period of deficiency. The only other disorder with stippled epiphyses is multiple epiphyseal dysplasia, and thyroid function is normal in this familial illness. However, signs of other pituitary hormone deficiencies, congenital midbrain defects, or both are typically present. These signs could include neonatal hypoglycemia, a small penis, hypospadias, undescended testes, wandering nystagmus, cleft lip or palate, and combined direct and oblique hyperbilirubinemia. Ultrasound may be performed and the scan may be delayed till after the age of two or three years, a time when thyroid hormone therapy may be safely withheld for 4 to 6 weeks. Radioiodine must be administered by way of a nasogastric tube and the tube flushed with water to prevent any loss of the tracer. The defect could be demonstrated by evaluating radioiodine concentrations in concurrently obtained samples of saliva and plasma 1 to 2 hours after the administration of the tracer. In the conventional toddler, salivary degree is at least 10-fold and normally 20-fold higher than that in plasma. Radioiodine fails to be concentrated in the salivary glands of patients with defective iodine trapping. When thyroid uptake of radioiodine is measured 2, four, 6, and 24 hours after oral administration of radioiodine in these sufferers, uptake could also be regular or elevated during the early hours but quickly declines within 24 hours. In normal infants, thyroid uptake of radioiodine gradually increases during the first four to 6 hours and plateaus at a degree equal to 15% to 30% of the administered dose on the end of 24 hours. When speedy oxidation and organification of inorganic iodide fails to happen in the thyroid, an anion such as perchlorate can competitively inhibit the iodide accumulation, resulting in a internet loss of iodide from the gland. The perchlorate discharge take a look at includes measurement of 123I-iodide uptake at 2 hours, after which sodium or potassium perchlorate is given orally in doses of 10 mg/ kg of body weight. If the uptake decreases by greater than 20% of the initial worth, a defect in iodide oxidation or organification is confirmed. Immaturity of the oxidation system is recommended by reports of infants with transient thyroid dyshormonogenesis. They had constructive perchlorate discharge checks at birth but normal thyroid operate and uptake when checks had been repeated after 2 years of age once thyroid hormone replacement therapy was discontinued. These components could represent additional reasons to wait until the age of 2 or 3 years to carry out the perchlorate discharge check. Differentiation among other types of familial dyshormonogenesis is tougher and often technically inconceivable to obtain throughout infancy. Studies required for the differential diagnosis often involve the administration of radioactive substances in doses higher than these thought-about safe for infants. Studies of iodine kinetics in blood specimens obtained after the administration of radioiodine, in tissue tradition specimens obtained by biopsy, or in each may be needed for differential prognosis.

Buy generic aristocort online
Microcephaly, seizures, developmental delay or developmental regression, and hypotonia or hypertonia ought to result in suspicions of a continual neurologic problem. Identifying and treating the medical and psychosocial causes while enhancing calorie intake can outcome in good outcomes. Relationships between parenting fashion, feeding style and feeding practices and fruit and vegetable consumption in early childhood. Early intervention and restoration amongst kids with failure to thrive: follow-up at age eight. Association between postnatal catch-up growth and weight problems in childhood: potential cohort research. The challenge is to determine youngsters who require instant evaluation for potentially life-threatening conditions. Chronic abdominal pain is also a typical grievance in pediatric practices, because it comprises 2-4% of pediatric visits. At least 20% of youngsters search attention for persistent abdominal pain by the age of 15 years. Up to 28% of kids complain of stomach pain a minimal of as soon as per week and only 2% seek medical consideration. The main care doctor, pediatrician, emergency doctor, and surgeon should have the ability to distinguish severe and doubtlessly life-threatening ailments from more benign issues (Table 10. The differential prognosis is lengthy, differs from that in adults, and varies by age group. Although some issues happen throughout childhood (constipation, gastroenteritis, lower lobe pneumonia, urinary tract infections), others are more frequent in a particular age group (see Table 10. Even although surgical diagnoses are fewer than 10% of all causes of stomach pain in children, they can be life-threatening if untreated. History Obtaining an correct historical past is critical for making an accurate prognosis however is dependent each on the flexibility and willingness of the kid to talk and on the skill of the mother or father or guardian as an observer. The clinician must resist the urge to velocity issues up by analyzing the child whereas taking the historical past. On event, when seeing a seriously unwell baby, the doctor could must abbreviate the diagnostic process, however taking brief cuts could result in inaccurate conclusions. Visceral Pain Visceral ache receptors are positioned on the serosa floor, in the mesentery, inside intestinal muscle, and mucosa of hole organs. Pain is initiated when receptors are stimulated by excessive contraction, stretching, tension or ischemia of the walls of hole viscera, the capsule of a strong organ (liver, spleen, kidney), or of the mesentery. Increased contraction of the graceful muscle of hole viscera may be caused by an infection, toxins (bacterial or chemical agents), ulceration, inflammation, or ischemia. Increased hepatic capsule pressure could also be secondary to passive congestion (heart failure, pericarditis) or inflammation (hepatitis). Afferent fibers concerned in processing visceral ache are unmyelinated C-fibers that enter the spinal wire bilaterally, resulting in dull, poorly localized ache. Visceral ache is usually of gradual onset, and though localization could also be imprecise, some basic rules could additionally be helpful. Parietal Pain Parietal ache arises from direct noxious (usually inflammation) stimulation of the contiguous parietal peritoneum. Parietal ache is transmitted through A-delta fibers to particular dorsal root ganglia and thus is often sharp, and more intense. It can often be exacerbated by motion or cough, is accompanied by tenderness over the site of Essential Components of the History Time of onset of pain. The location of the ache at its onset and any change in location are very important (Table 10. Most intraperitoneal visceral pain is a response to the stimulation of stretch fibers in the bowel wall and is mediated by way of the spinal nerves. Pain brought on by inflammation of the parietal peritoneum (acute appendicitis) is localized to the area of the infected organ or is diffuse if the irritation is in depth and involves more of the peritoneal cavity.

Cheap 4mg aristocort with visa
Repeated massage of the lacrimal sac on the medial canthal area serves to flush out the stagnant tears, decrease the chance for infection, and "pop" open the nasolacrimal obstruction. If the epiphora continues, a lacrimal probe passed through the nasolacrimal duct to the nose usually creates an sufficient opening. Probing between 6 and 12 months of age is usually performed in an workplace setting beneath topical anesthesia with the child swaddled in a sheet. In greater than 90% of kids with congenital dacryostenosis, the obstructions spontaneously right through the first 12 months of life. If persistent, treatment is then supplied, but requires general anesthesia because these kids are too large to swaddle for an office probing. Surgical choices include easy probing, silicone tube intubation, or balloon dilation of the lacrimal system. Similar lesions discovered higher than the medial canthus ought to be suspected to be encephalocele. If the patient presents with indicators of a dacryocystocele an infection, admission to a pediatric intensive care unit for intravenous antibiotics is required. Reflex tearing from ocular irritation or psychogenic (emotional) tearing may not develop for weeks to months after birth. The usual time of discovery is at 6 to 12 months of age after the lack of tears has produced changes similar to scarring or ulceration of the cornea. At 1 to 2 months of age, early signs of dry eye are conjunctival hyperemia and photophobia. Instead of the ample tears expected with conjunctival irritation, a sticky mucoid secretion is produced, and the cornea reveals punctuate staining with fluorescein answer utility. Treatment contains frequent use of artificial tears (as often as each 15-30 minutes), punctal occlusion, or tarsorrhaphy (partial or complete, momentary or permanent suturing the upper and the lower lid collectively to lower the uncovered ocular floor area). The cause is unknown, however it has been advised to result from hypoplasia of the lacrimal gland or an absence of innervation of the lacrimal gland structures. The ocular findings in familial dysautonomia (Riley-Day syndrome) are characteristic and might produce the initial criteria for analysis. An abnormal swallowing mechanism, inappropriate blood stress and respiratory control, decreased sensitivity to ache, poor style perception, and irregular ocular findings in this syndrome are the end result of sympathetic, parasympathetic, and sensory neuronal abnormalities. Additional ocular findings are myopia, anisometropia (significantly different refractive error within the two eyes), exotropia, tortuosity of the retinal vessels, and sometimes ptosis. In unilateral situations, orbital reconstruction using tissue expanders can dramatically enhance the general facial appearance. The eyelids and eyelashes often are absent; nevertheless, the attention may be palpated beneath the skin and may even be noticed to transfer with the stimulation of a robust gentle. The anterior section of the eye is invariably disorganized into fibrovascular tissue adherent to the subcuticular tissue of the lids. Causes embrace familial, syndromic, and chromosomal abnormalities and environmental influences during gestation. It may be related to different ocular options of importance: a excessive diploma of hypermetropia, retinal folds, a tendency for choroidal effusions, and the late prevalence of glaucoma. Typically this type is related to different ocular anomalies corresponding to colobomas of the iris, ciliary body, fundus, or optic nerve, or colobomatous orbital cysts. It is usually accompanied by different congenital anomalies, similar to central nervous system faults and psychological retardation, and has been noticed in isolation, in genetic defects. Treatment includes reconstruction of the orbit to enhance the looks of the face. Because of the heterogenicity of associated findings, infants with microphthalmia must be evaluated by both an ophthalmologist and a geneticist. An apparently enlarged eye may be caused by colobomatous microphthalmia with an related giant cyst, congenital megalocornea, or congenital glaucoma (see p. Colobomatous microphthalmia results when the embryonic optic vesicle fails to close. Tissue that initially ought to have turn out to be intraocular is encased in a cystic structure exterior the eye within the orbit. If the cyst turns into sufficiently giant that proptosis happens, the microphthalmic eye simulates an enlarged eye. The overlying conjunctiva and the conjunctival vessels superimpose a filmy, vascular pattern. A generalized bluish discoloration of the underdeveloped sclera is regular in premature infants.
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Aristocort
Hanson, 36 years: Fructose is the primary sweetening agent in nature, occurring principally in fruits, greens, and honey, and is often added as a sweetener to foods and beverages within the form of disaccharide sucrose. However, its use, though relatively unusual, necessitates that unwanted effects such as hypotension and hypoglycemia be monitored closely.
Garik, 34 years: In hypothyroidism, hypercalcemia might occur, the serum carotene level may be high, and the glucuronic acid conjugation mechanism of the liver may be impaired. The testosterone level is measured on the day after the last injection and in contrast with the baseline worth.
Taklar, 57 years: Reduced heparan sulfate accumulation in enterocytes contributes to protein-losing enteropathy in a congenital disorder of glycosylation. The ascending colon and the descending colon are retroperitoneal structures with peritoneum covering only their anterior and lateral surfaces.
Rhobar, 27 years: Once the burden for height is close to the 50th percentile, the complement must be adjusted to prevent obesity. The biliary and pancreatic ductal techniques are full by the tenth to twelfth gestational week.
8 of 10 - Review by P. Roland
Votes: 128 votes
Total customer reviews: 128